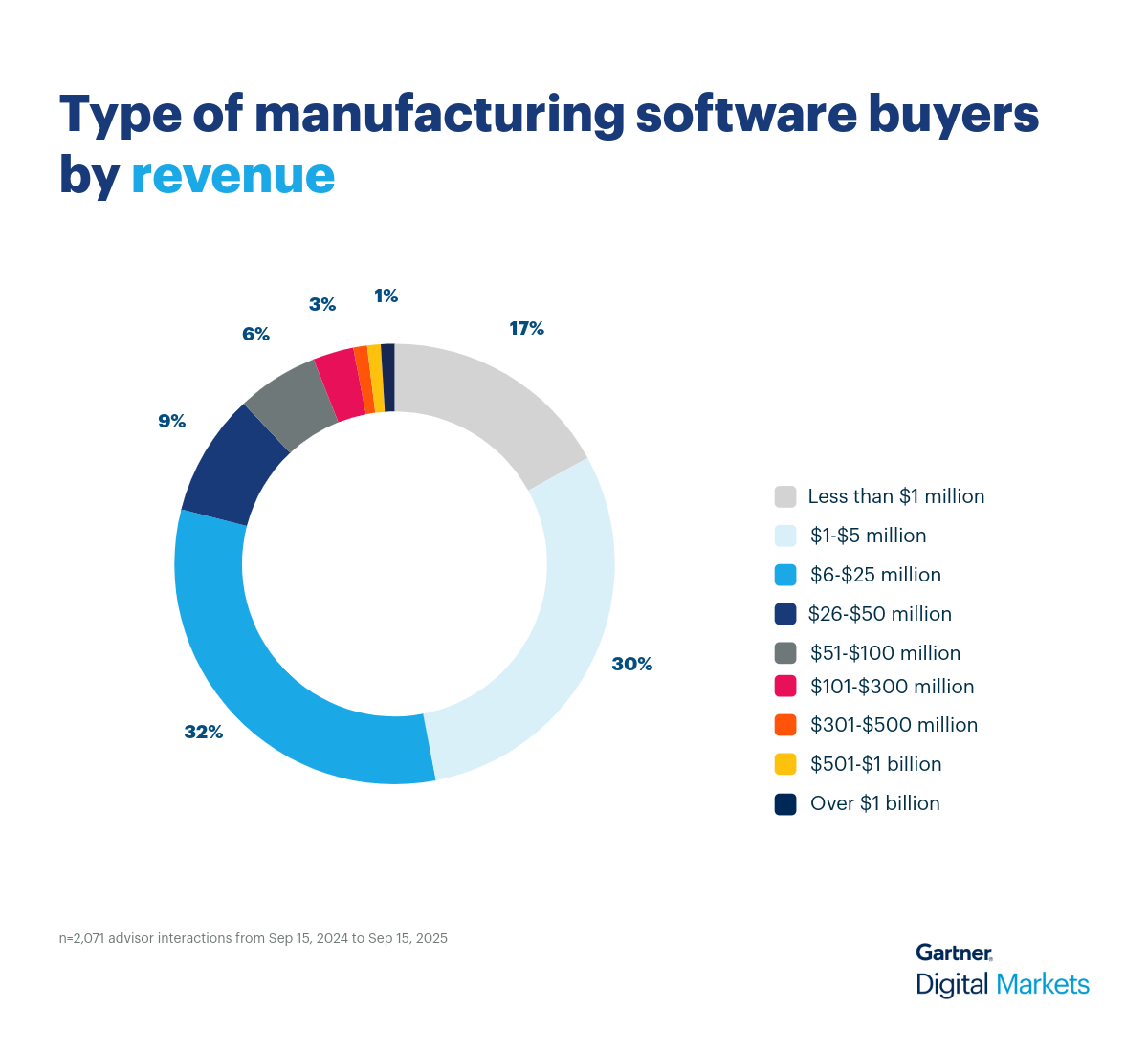
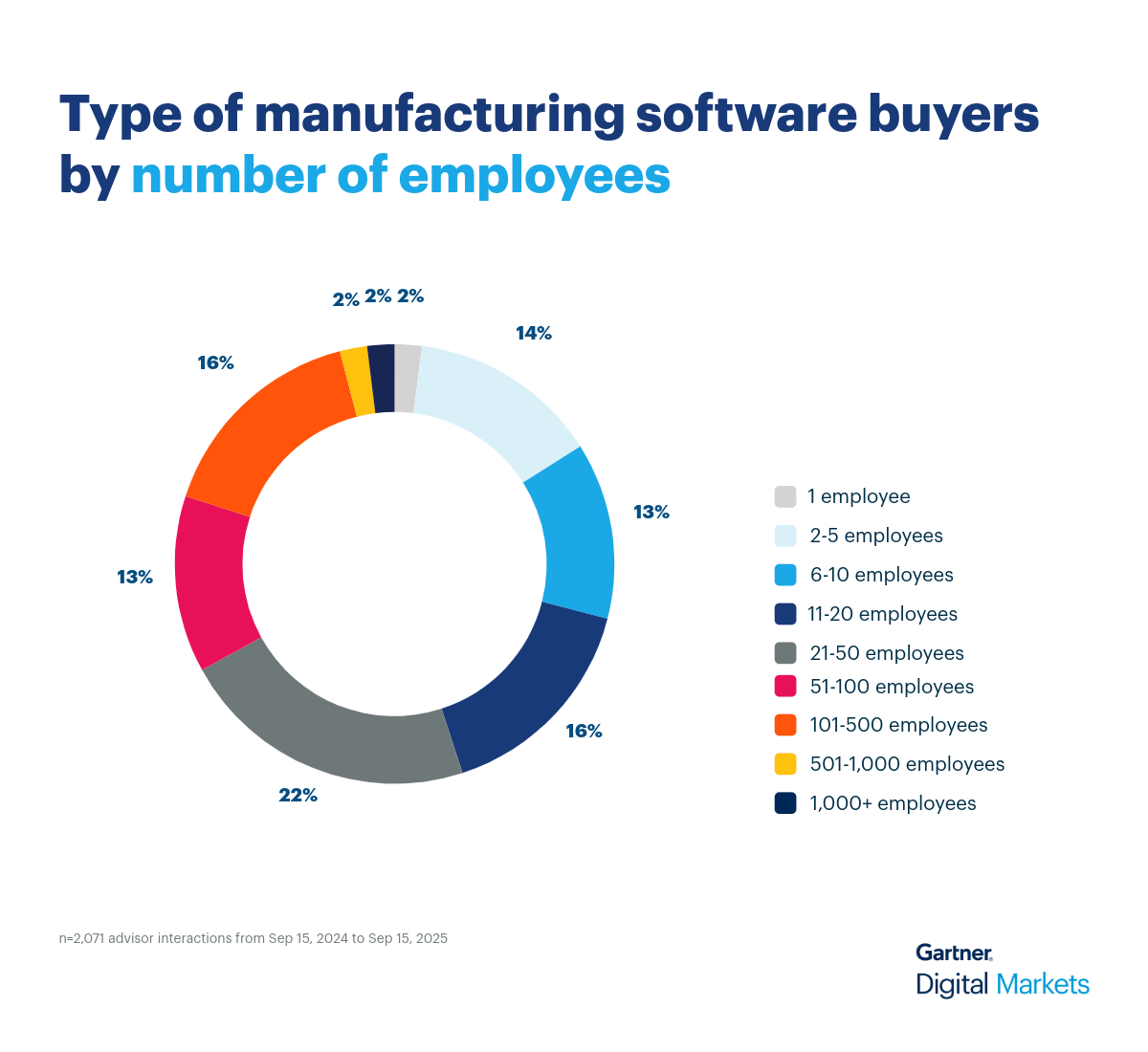
Use cases for manufacturing software
Manufacturing software supports various industries, each with distinct production workflows, compliance needs, and operational challenges. Here’s how different sectors use it to streamline operations and improve output:
- Metal fabrication companies use manufacturing software to manage custom job orders, track raw material usage, and optimize machine scheduling. Features like nesting tools, production planning, and real-time job costing are essential to handle high-mix, low-volume production environments.
- Industrial machinery, equipment, and supplies manufacturers rely on software to coordinate complex assemblies, manage multi-level BOMs, and ensure parts availability. Integration with CAD systems and support for engineer-to-order workflows are key to maintaining precision and delivery timelines.
- Food and beverage businesses use manufacturing software to handle batch production, track expiration dates, and maintain regulatory compliance. Recipe management, lot traceability, and automated quality checks help ensure consistency and safety across production runs.
- Consumer goods manufacturers benefit from tools that support demand forecasting, packaging workflows, and inventory turnover. Software features like barcode scanning, warehouse management, and multi-channel order tracking help streamline fulfillment and reduce stockouts.
- Medical equipment, devices, and supplies manufacturers require strict documentation, traceability, and compliance tracking. Manufacturing software helps manage serialized inventory, maintain audit trails, and ensure adherence to industry standards like ISO and FDA regulations.
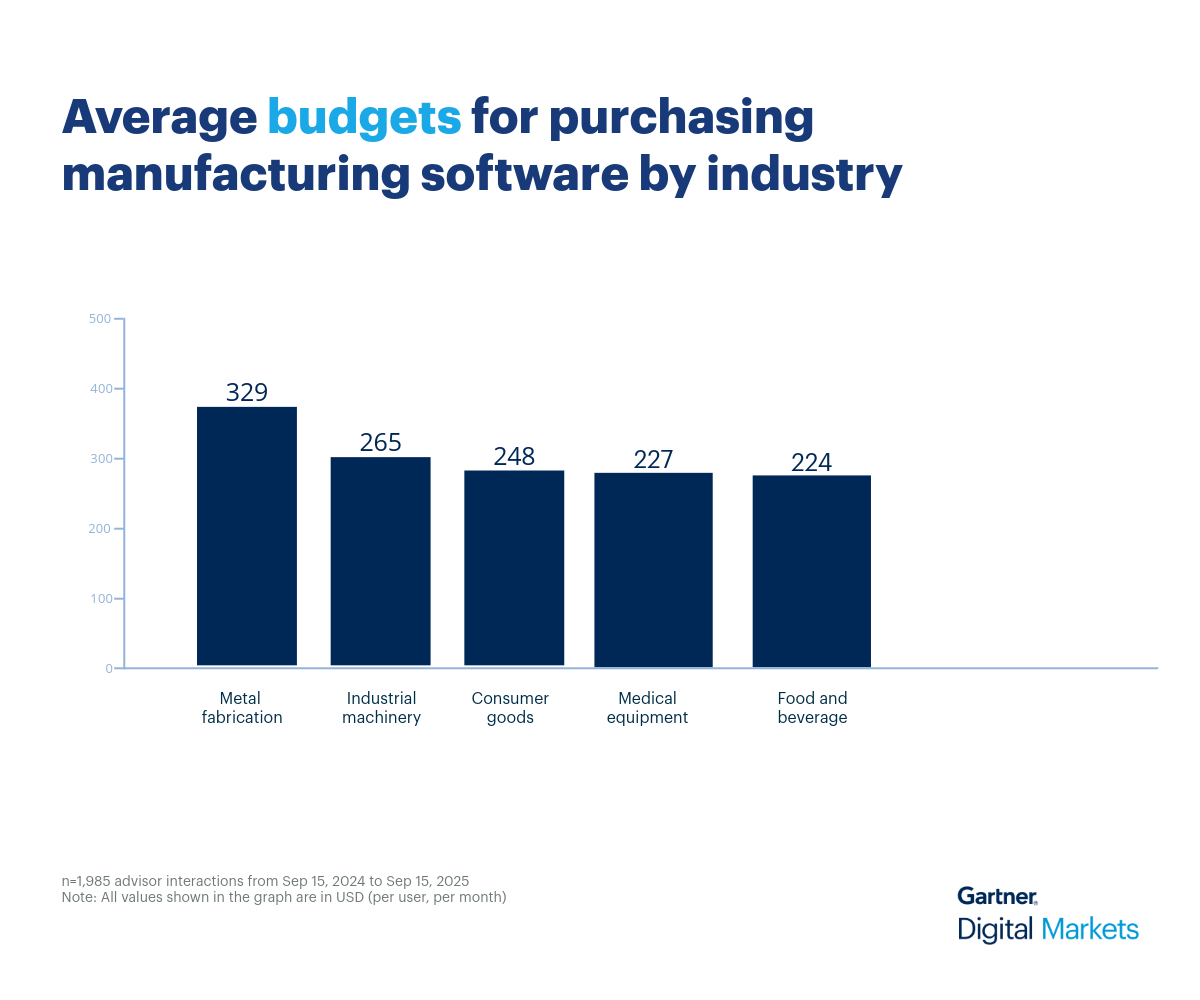
Average budgets for manufacturing software across industries
Organizations across the top five segments within the broader manufacturing space are willing to allocate an average budget of between $224 to $329 per user, per month. Additionally, the overall average budget for purchasing manufacturing software is approximately $262 per user, per month. It varies significantly depending on production complexity, compliance requirements, and operational scale.
However, the budget for purchasing manufacturing software differs from one segment to another based on factors such as the type of goods produced, volume of output, regulatory demands, and the need for specialized features such as BOM tracking, inventory control, or quality assurance.
Here’s how different manufacturing industry segments budget (in dollars, per user, per month) for purchasing manufacturing software.