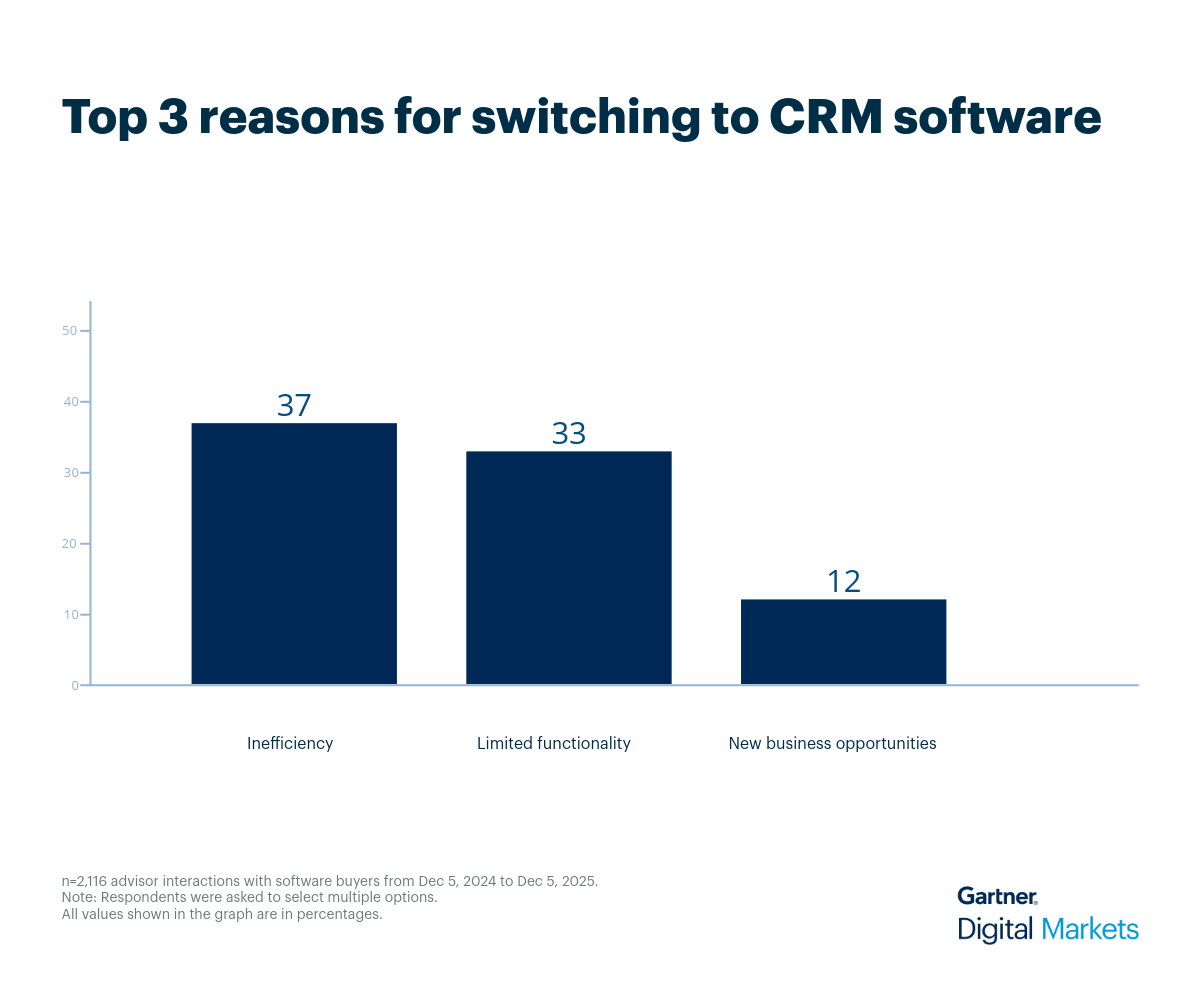
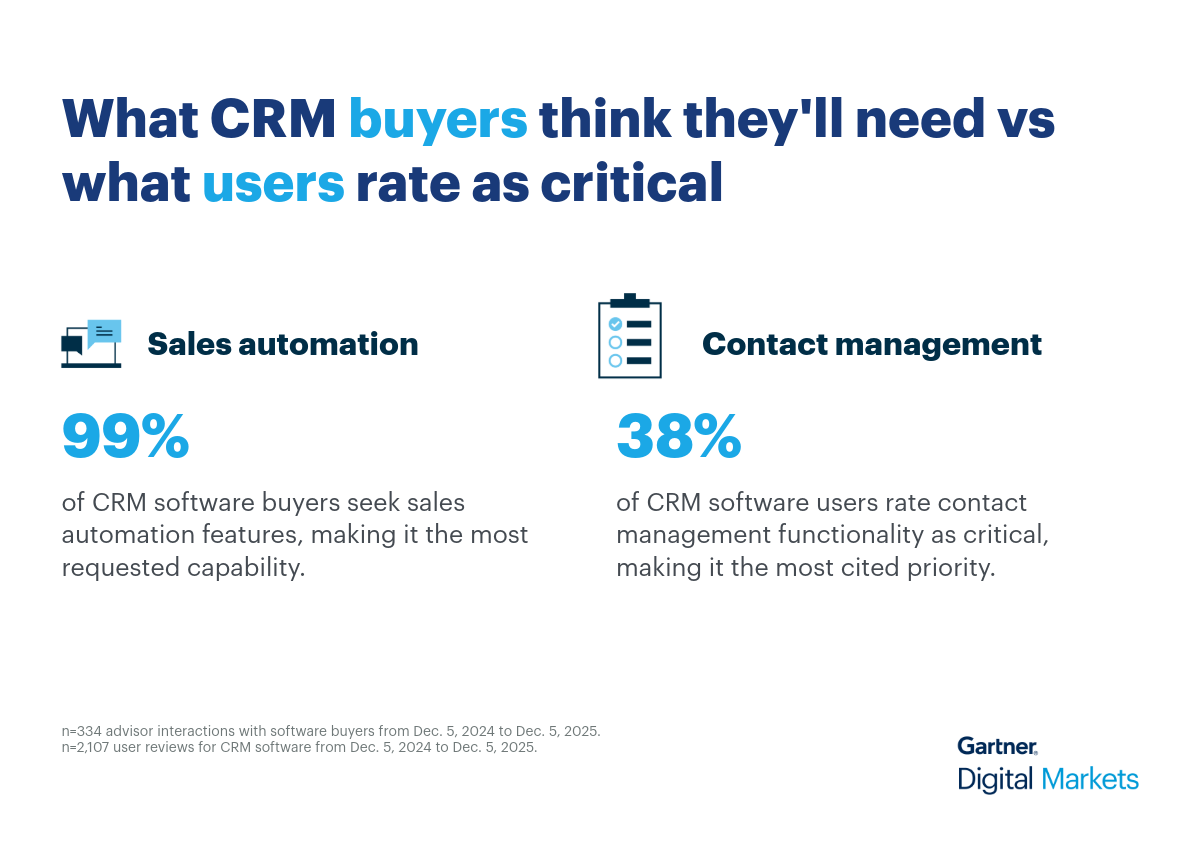
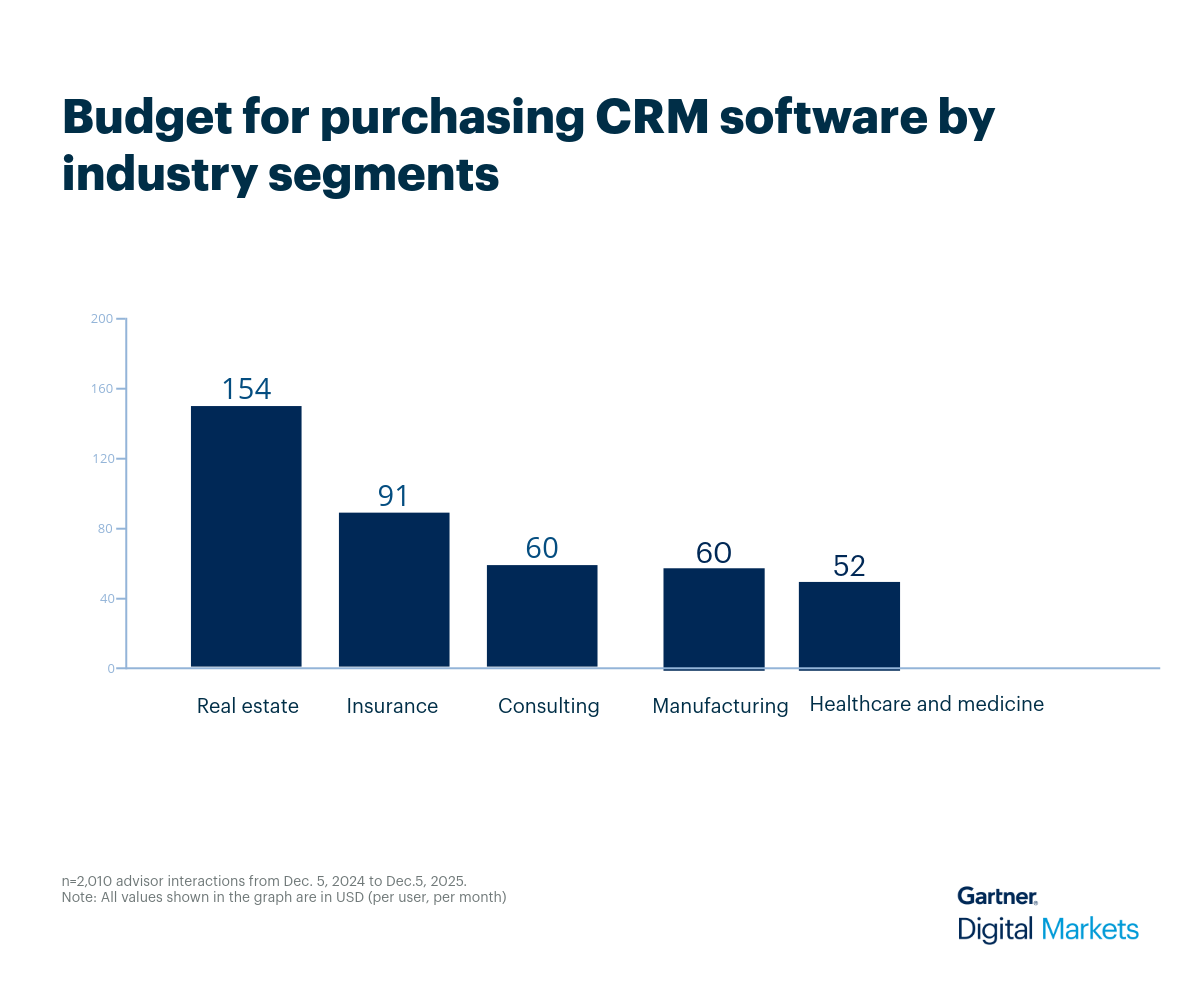
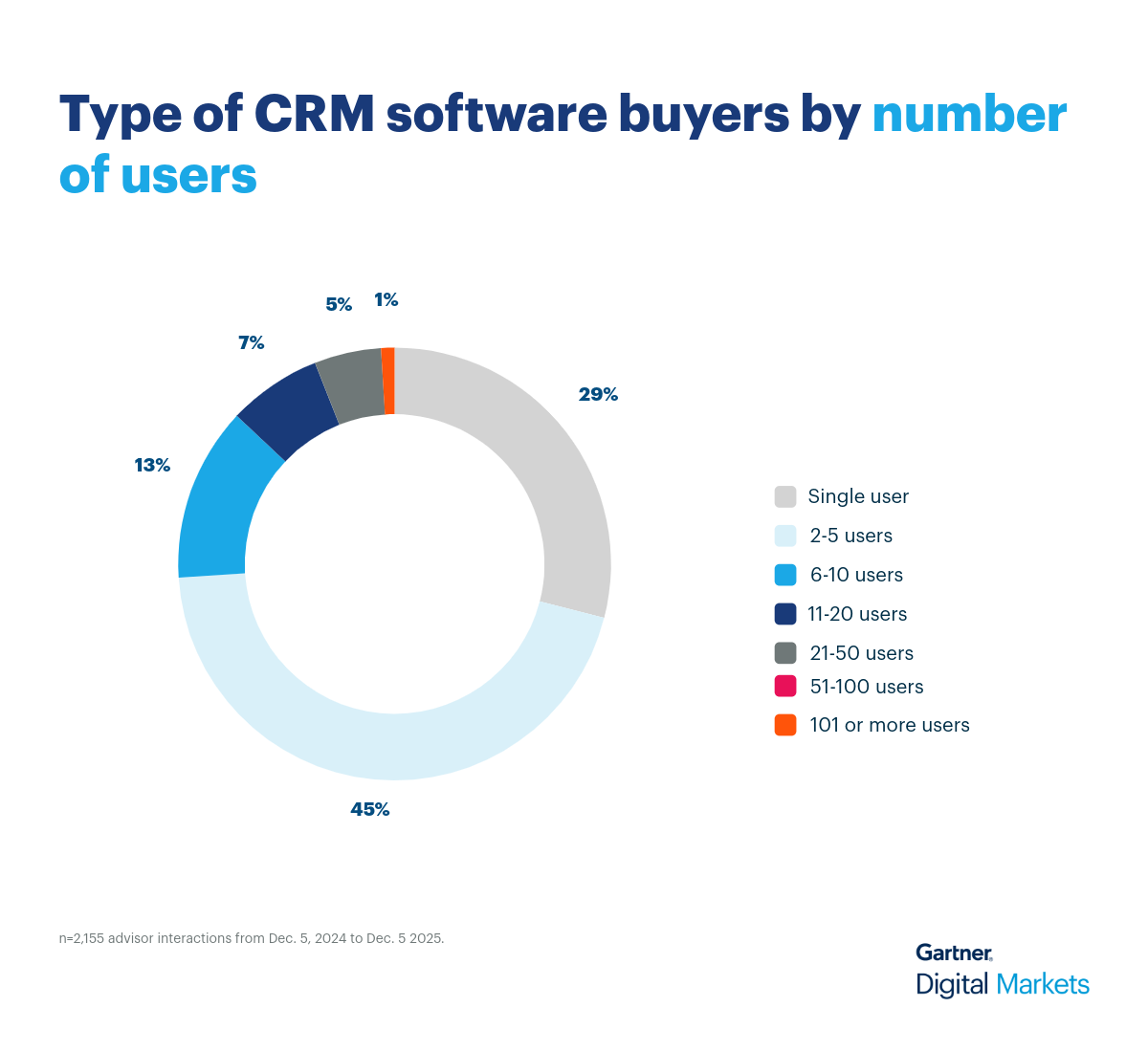
CRM software is no longer just a contact database—it’s a strategic tool for driving engagement, improving retention, and uncovering revenue opportunities. But as priorities shift mid-implementation such as balancing automation with human touch—choosing the right CRM becomes a challenge that impacts long-term growth. This growing complexity also means vendors must compete harder for visibility and trust.
With a multitude of tools on Gartner Digital Markets’ buyer destination sites—Capterra, GetApp, and Software Advice–how can vendors ensure they stand out and get their fair share of buyer attention?
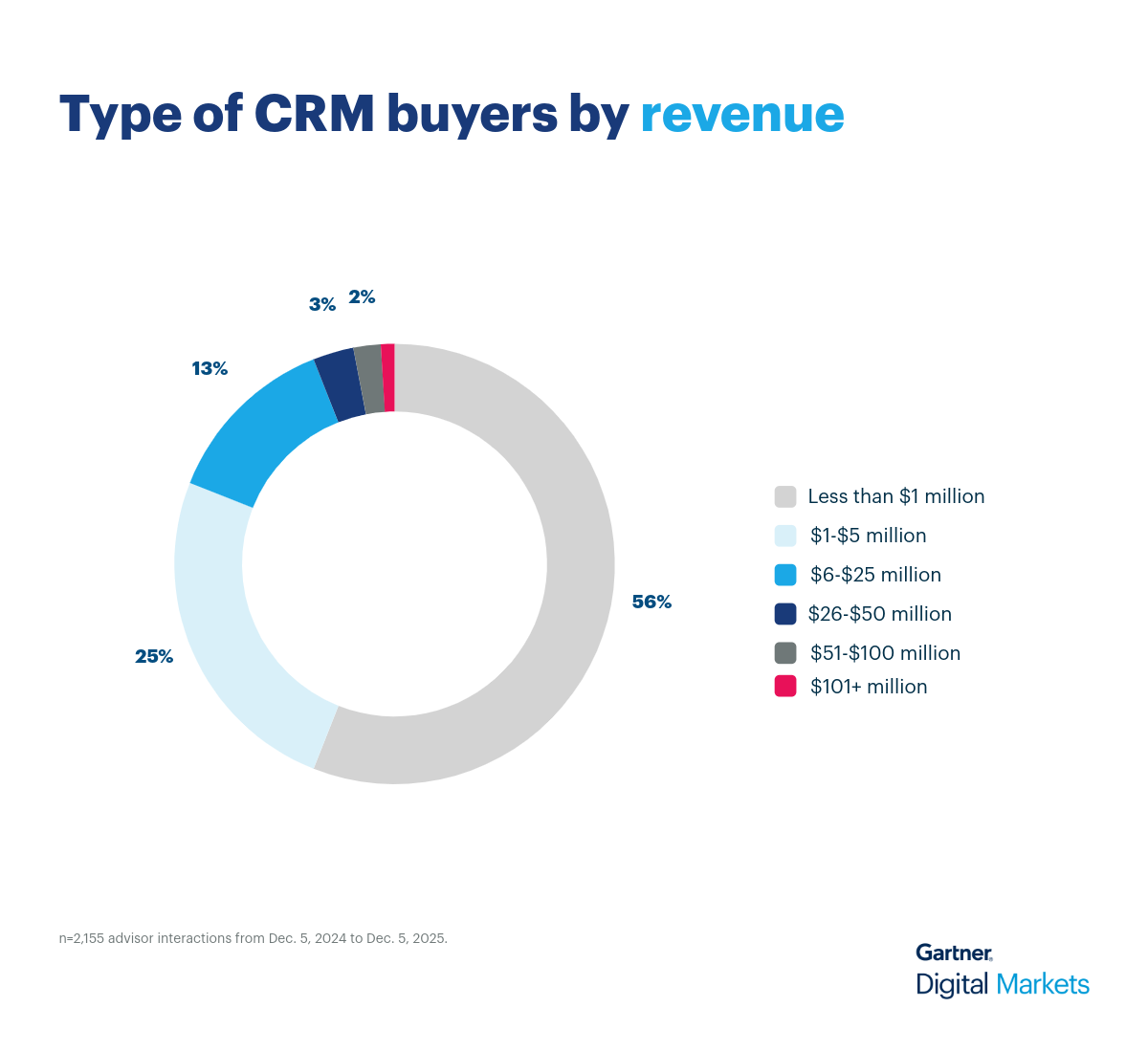
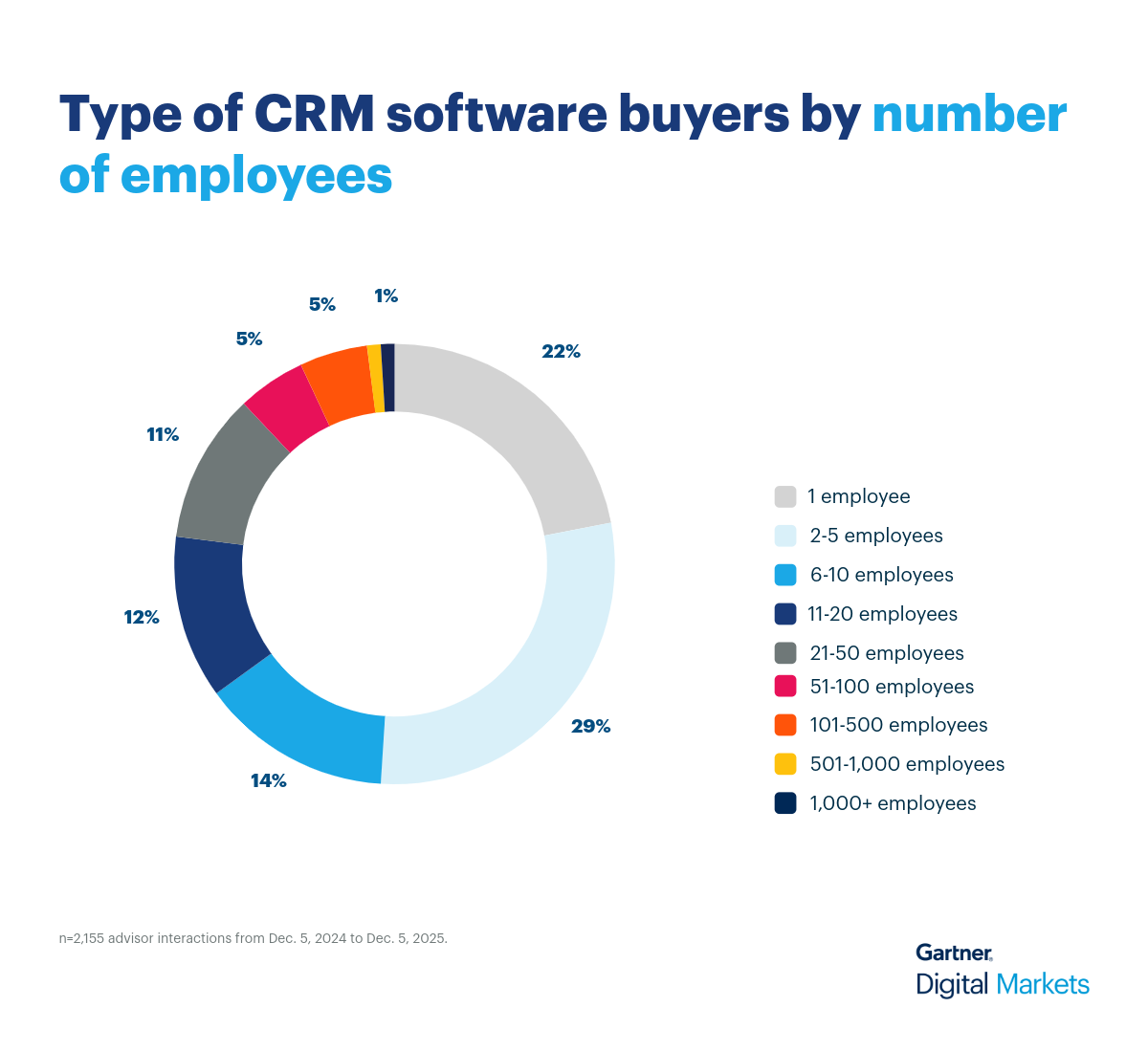
Our software advisors speak with thousands of buyers every year, qualifying them based on budget, authority, need, and timeline (BANT). We’ve analyzed these real buyer conversations to help vendors sharpen their messaging and position their CRM software to match what buyers are actually looking for.