Gartner warns tech product leaders of the potential for damaging market-share losses if they fail to develop preemptive cybersecurity solutions.
- Gartner client? Log in for personalized search results.
Why preemptive cybersecurity solutions are key in the AI race
AI puts cyberattacks in overdrive. Traditional detection-and-response cybersecurity methods can’t keep up with the surging threats from bad actors leveraging AI. Preemptive cybersecurity solutions defend more effectively within the emerging global attack-surface grid against these more sophisticated AI-enabled attackers. This proactive approach represents a shift from traditional reactive methods to preemptive measures aimed at mitigating risks before they escalate. The integration of such capabilities is crucial for serving end users effectively.
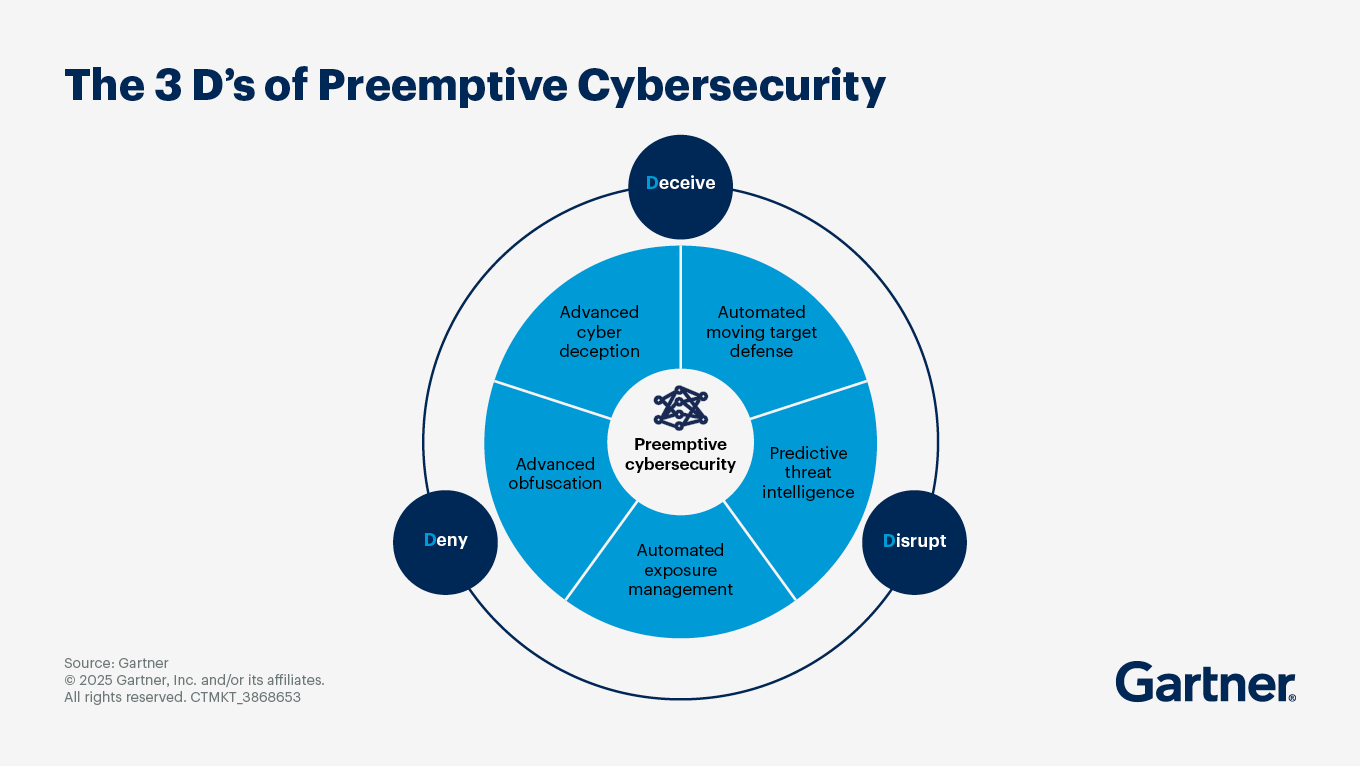
Product leaders who fail to invest in preemptive cybersecurity capabilities risk career-impacting cyber incidents and the potential for damaging market share losses within the next two to four years. Gartner advocates a three-pronged approach called “The 3 D’s of Preemptive Cybersecurity” (see image above).
Gartner has developed a unique collection of guidance for product leaders competing within and across the layers of the modern AI tech stack. (Clients: Sign in to enter the Gartner AI Vendor Race Microsite directly.)
Why and how preemptive cybersecurity solutions must deny, deceive and disrupt attackers
Gartner urges product leaders to pursue a preemptive approach to defend against weaponized AI by framing their strategy around the “three D’s” of preemptive cybersecurity.
Microsoft SharePoint “zero-day” vulnerability clearly illustrates the challenges of defending against emerging AI-enabled threats
The current cybersecurity challenge is twofold:
How to secure AI applications from novel threats such as disinformation
How to leverage AI capabilities to defend against a rapidly expanding attack surface — known as the global attack surface grid
One well-publicized example in late July 2025 was the active exploitation of a zero-day vulnerability in Microsoft’s on-premises SharePoint Server software. This vulnerability allows attackers to bypass authentication and execute code remotely on vulnerable, on-premises SharePoint servers to deploy web shells, while maintaining persistent access to the affected servers. Once they establish an initial foothold, attackers can execute additional arbitrary commands, download files and potentially move laterally within the network undetected. To make matters worse, leveraging this same vulnerability, attackers could also extract the server's cryptographic “machine keys” and then forge their own authenticated requests, while maintaining access, even after the initial vulnerability is detected and patched, and any detected malicious web shells are removed.
This case highlights the core challenge of defending against zero-day vulnerabilities wherein attackers find and exploit previously unknown software vulnerabilities before software vendors and end users have a chance to identify and patch them (giving them “zero days” to respond).
Preemptive cybersecurity technologies build resilience against such attacks by focusing on prevention, not reaction. And as the AI vendor race heats up, Gartner expects that by 2030, preemptive cybersecurity solutions will make up 50% of IT security spending, replacing traditional stand-alone detection-and-response solutions as the preferred defense against cyberthreats. These solutions must deny, deceive and disrupt would-be attackers.
Deny entry with a preemptive shield
Bar intruders from accessing emerging technology solutions within the global attack surface grid by using a combination of automated exposure management and advanced obfuscation technologies, which can continuously find and patch vulnerabilities while concealing code and sensitive data with advanced encryption techniques. This renders assets and resources invisible to attackers through cloaking and advanced segmentation enclaves.
Advanced obfuscation technologies align with zero-trust principles by assuming that threats can originate internally and externally and requiring explicit verification for access. They don’t just deny unauthorized access; they identify potential threats more quickly and accurately.
These technologies represent a unique control point for accessing sensitive data in protected environments, offering real-time observability. They act as an early detection system for unauthorized access attempts or tampering.
Advanced obfuscation is critical for organizations seeking resilience against ransomware, advanced persistent threats (APTs) and AI-driven cyberattacks.
Deceive bad actors
Use decoys, misdirection and illusion to throw malicious actors off the scent. For example:
Advanced cyber deception (ACD) solutions leverage a variety of deceptive elements to lure attackers away from critical systems and essentially create a “cyber minefield” for attackers. These platforms create realistic decoys, such as fake servers, applications or files, that mimic production systems, enticing attackers to interact with them. By analyzing attacker behavior on these decoys, organizations can then quickly gain valuable insights into attacker tactics and techniques and then use that information in real-time to immediately improve their overall security defenses.
Automated moving target defense (AMTD) solutions operate by constantly changing a system’s configuration, making it a “moving target” for attackers. This can involve randomizing memory addresses, altering network configurations or modifying software components. AMTD leverages automation to dynamically adjust system configurations, ensuring a continuous and unpredictable environment. This often involves AI and machine learning to adapt to intelligence collected on new emerging threats and optimize defense strategies. To further deceive attackers, AMTD is often combined with the use of advanced cyber deception to add even more layers of “moving targets.”
Disrupt attacks
Anticipate and prepare for emerging threats rather than waiting for attacks and then doing damage control after the fact. For example, use:
Predictive threat intelligence (PTI). These platforms continuously collect information from a wide variety of sources — like security alerts, public online discussions, the dark web and records of past cyberattacks. Then, using a combination of advanced analytics, AI and machine learning, PTI solutions sift through all that data to spot emerging threats, understand how hackers operate and find weaknesses before they can be exploited. PTI platforms can also predict which threats are most likely to target your specific organization. They do this by considering things like what business you’re in, the technology you use and how visible you are online. With these predictions, your organization can address vulnerabilities and exposures to boost your defenses before an attack even happens, keeping your digital assets much safer.
Automated exposure management. These solutions offer capabilities for continually assessing attack surfaces, and prioritizing vulnerabilities and exposures for remediation. In today’s complex technology environment — spanning multicloud, hybrid infrastructure and AI-enabled emerging technologies — managing vulnerabilities manually in a timely manner is impossible. Automated exposure management tools offer scalable, continuous monitoring across all parts of this environment. The automation assures real-time, contextualized insights into an organization’s exposure landscape. This allows more informed threat hunting, more accurate risk prioritization and more timely, actionable guidance for remediation.
What product leaders should know about preemptive cybersecurity
Gartner urges product leaders to become fluent in preemptive cybersecurity capabilities and protocols to ensure products — and their pricing — deliver customer value and contribute to growth.
Key actions include:
Leverage AI for preemptive cybersecurity. Use emerging technologies to deny, deceive and disrupt cybercriminals before they can initiate their objectives — and to ensure security-product capabilities stay ahead of emerging threats.
Understand the emerging global attack surface grid and related AI-enabled threats. Recognize that the global attack surface grid is rapidly expanding and includes multicloud environments, Internet of Things (IoT) smart devices, data networks and APIs, blurring the lines between internal and external assets, and emerging technologies introduce new and novel attack vectors every day. Additional recommended reading for Gartner clients: Quick Answer: What Is the Global Attack Surface Grid?
Secure AI-enabled applications. GenAI apps introduce significant new security and privacy risks — especially since exposures often take enterprises up to three months to identify and address.
AIign AI security product and pricing capabilities to business goals. Product leaders navigating AI-enhanced security offerings, especially those with AI agents, face the complex challenge of effectively pricing and positioning solutions amid uncertain operating costs, unpredictable customer usage and AI’s evolving perceived value.
How preemptive cybersecurity aids the end user
This preemptive approach shifts security from “detect-and-respond” to prevention, embedding predictive analytics, continuous exposure management and automated mitigations into operating systems, networks, applications and services, so users face fewer successful attacks and less disruption.
Direct user-facing benefits
Fewer successful breaches and reduced attack likelihood. Preemptive controls make it harder for attackers to find or exploit assets, lowering breach frequency and impact for end users.
Proactive neutralization of emerging threats. Preemptive cybersecurity strategies and solutions focus on identifying the precursors of an attack before a breach occurs. By leveraging high-fidelity signals for immediate intervention, security teams can neutralize emerging threats before they mature, effectively breaking the kill chain and preventing downstream disruption.
Lower financial and compliance risk to users (and customers). Preventing incidents reduces breach-related costs, lowers potential insurance premiums and improves audit/posture scores that affect customers and business continuity.
Preemptive cybersecurity FAQs
What is preemptive cybersecurity?
Preemptive cybersecurity is an emerging but increasingly critical approach that aims to prevent and deter cyberattacks before they can launch or succeed, instead of responding to attacks already underway. Gartner advocates that preemptive cybersecurity solutions incorporate capabilities to: 1) Deny attackers the opportunity to initiate attacks or access desired resources; 2) Disrupt ongoing attacks as they occur, and 3) Deceive attackers to divert them from critical assets.
What is the global attack surface grid?
Today’s attack surface has evolved from a perimeter-based concept to a global view of all possible entry points. The global attack surface grid comprises the complex network of physical and digital technology assets and resources that span the globe, and represent all potential entry and pivot points where a threat actor might attempt to compromise, manipulate or control these assets and resources for malicious intent.
What are cyber exposure dimensions?
The cyber exposure dimensions represent specific aspects of assets, resources or operations that are vulnerable to common threats and attack vectors in a certain context. They include physical exposure, digital exposure, social exposure and electromagnetic exposure.
Attend a Conference
Join Gartner experts and your peers to accelerate growth
Join the leading technology and service provider peers to get an update on accelerating tech growth in a new era of transformation and technology trends.
Gartner Product Leadership Conference
Grapevine, TX

Drive stronger performance on your mission-critical priorities.