Great self-service customer service needs a holistic strategy across touchpoints.
- Gartner client? Log in for personalized search results.
Self-Service Customer Service: Key Capabilities and Strategies
Transform your self-service customer service strategy with these core capabilities
Modern CX demands a self-service-first mindset. Yet most self-service experiences are unsuccessful, leaving customers frustrated while increasing organizational costs. Download the 11 foundational self-service capabilities to:
Understand the foundational capabilities that contribute to self-service customer support success
Identify gaps in your self-service capabilities and pinpoint areas of improvement
Expand your analytics reporting to understand the entire customer journey and identify bottlenecks
Meeting the needs of modern self-service customer service
To improve self-service success rates, prioritize CX and engagement, build integrated and robust capabilities and use the right metrics to measure your self-service effectiveness.
Modern Self-Service Needs
Future of Self-Service CX
Self-Service Metrics
Customers expect a lot from self-service, and too few get what they want or need
Customers expect a lot from self-service channels — more than them just being available 24/365. They want answers to myriad questions or issues, and information about products and services. But the average self-service customer support success rate today is just 14%. Improving this rate is a significant or moderate priority for 90% of customer service and support leaders Gartner recently surveyed.
But customer support teams must provide always-on problem solving across all of the self-service channels they offer — from site search to AI chatbots, to the portal to IVR and messaging apps.
To think about the entirety of the modern service delivery model — even as customer demands evolve — focus on a few key areas:
Prioritize CX and engagement. Organizations with the most successful self-service track record prioritize customer experience (CX) and customer engagement as much as reducing contact volume in assisted service channels. Focus on delivering a quality customer experience and addressing customer needs, and not just on deflecting calls.
Consider additional signals of customer demand, including surveys, clickstream analytics, and insight engines that track what users are searching for beyond incoming calls.
Treat self-service investments as products, not projects. Commit resources to continuously improve and update self-service capabilities after launch.
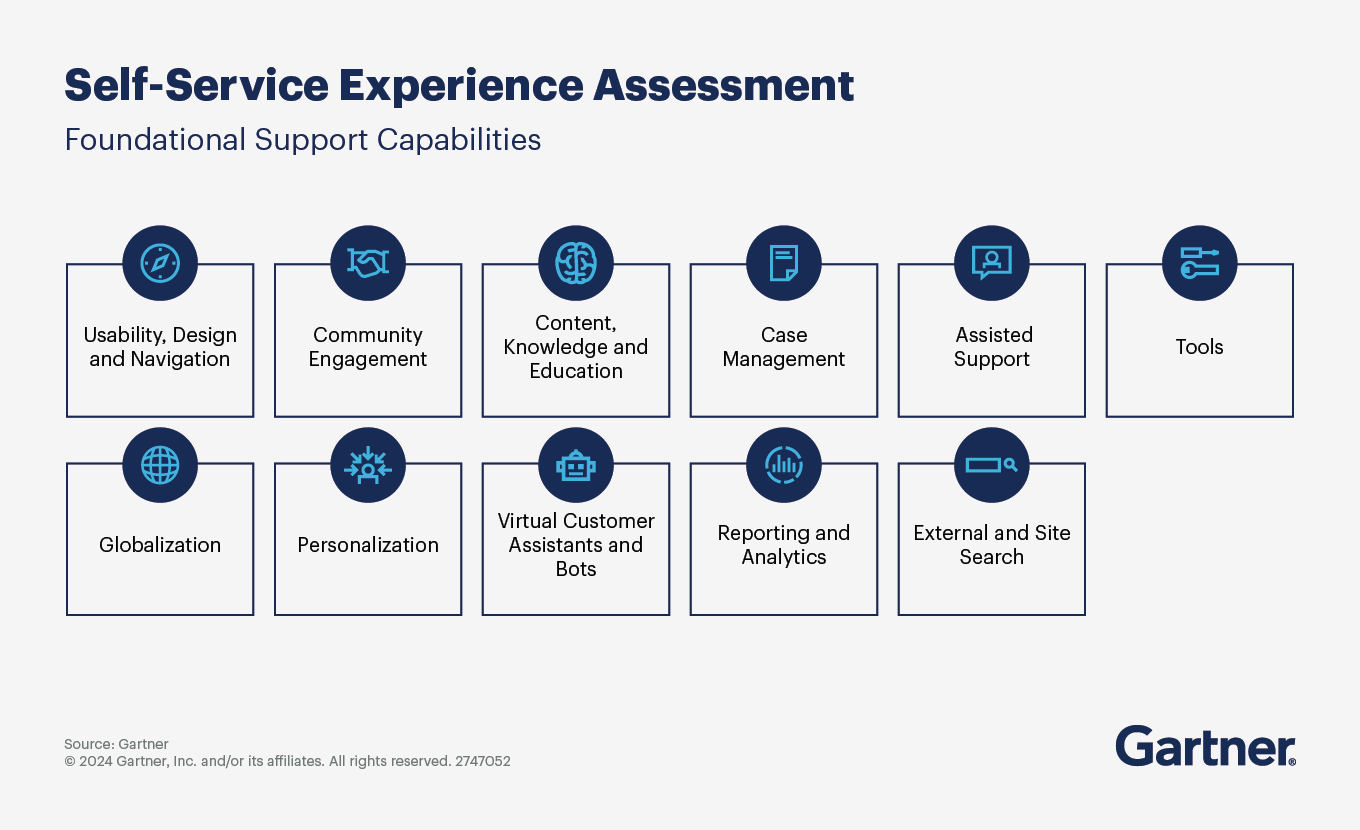
Gartner recommends that to meet the support organization’s goals and objectives, the self-service experience should include 11 foundational capabilities. Each improves some aspects of CX and elements of the search-to-resolution process. Together they drive significantly more business value, create effortless customer experiences and improve overall self-service adoption and success.
Here are the 11 capabilities:
External and site search. Provide content context, relevance and value in search results. Optimize for external search engines and include machine learning and AI capabilities.
Usability, design, and navigation. Ensure a consistent and user-friendly look and feel. Use predictable navigation menus, mobile responsiveness and accessibility.
Personalization. Enable customers to create profiles and tailor their experiences based on preferences, history and real-time behavior.
Globalization. Translate and localize menus, content and search experiences based on the customer’s language and locale.
Content, knowledge and education. Offer high-quality, customer-focused content that is easy to follow and provides direct answers to specific questions. Leverage rich media and feedback mechanisms.
Virtual customer assistants (VCAs) and bots. Deploy bots and virtual customer assistants to deliver information, perform transactions and engage in conversations.
Case management. Allow customers to submit details of their interactions or inquiries to assisted support via the self-service website. Integrate with CRM or case management solutions.
Assisted support. Provide human-based support options when self-service resolution fails or when customers require assisted support.
Community engagement. Create an online space for customers, associates, partners and experts to interact, share information and find knowledge.
Tools. Enable customers to carry out specific functions or tasks through self-service, such as ordering, scheduling, tracking or troubleshooting.
Reporting and analytics. Collect, measure and analyze self-service usage data and feedback. Use surveys, SEO, website analytics, clickstream analytics and customer journey analytics.
Assess your progress in creating compelling self-service experiences, using the Gartner Self-Service Experience Assessment.
Future self-service lies in a fully integrated customer experience
The problem today is that most digital self-service support experiences result in a dead end, requiring customers to create cases or escalate their requests to assisted support resources (which increases the cost per resolution).
Not surprisingly, then, customers don’t have much faith in self-service options. Fifty-three percent of customers Gartner surveyed said they go straight to an agent to resolve an issue. Only 20% of respondents did so because they didn’t think self-service was available.
Too often, customer service and support leaders treat self-service as ancillary to, and separate from, assisted service. They build self-service options as needed and without an overarching engagement strategy.
For many, self-service is represented as a series of technology projects rather than a program, integrated with assisted service and part of a broader customer engagement strategy.
Instead, self-service should be part of the overall customer engagement strategy. Customer service and support leaders must create a self-service program that works in tandem with assisted service, united under one service delivery model.
What the fully integrated future of self-service looks like
Future-state self-service is fully integrated into the organization’s customer engagement strategy. It provides an intelligent front door (IFD) (a starting point for the customer that captures their intent), serves up an answer or brings customers to the best resource to address their request. For example:
Product-based strategy. Self-service is treated as a product, not a project, with designated budget and resources. Content and capabilities are continuously maintained and promoted.
A seamless customer journey. Self-service and assisted service are unified under one customer service experience delivery model, and switching between the two is a seamless experience. An IFD acts as the default starting point for service. A seamless journey provides personalized content, actions and recommendations to guide customers to the right information or channel for their needs.
Customer journey success metrics. The organization uses a full range of metrics to gauge the customer journey’s effectiveness as a whole, including web analytics, clickstream analytics, journey analytics, and customer sentiment and feedback. Customer service and support works with other functions as needed to close feedback loops.
Fully incorporated technology ecosystem. An IFD employs both conversational AI and generative AI (GenAI) to provide natural language, individualized and personalized support. Customers can use an IFD to navigate their support options through advanced routing and next best action (NBA) capabilities. A technology roadmap ensures the continual improvement of self-service capabilities.
Aligned KM. Knowledge and content management are aligned with the needs of self-service. Insights and knowledge about the organization’s products and services are created and shared efficiently across self-service and assisted service. They are also continually updated to address, as well as anticipate, customer needs.
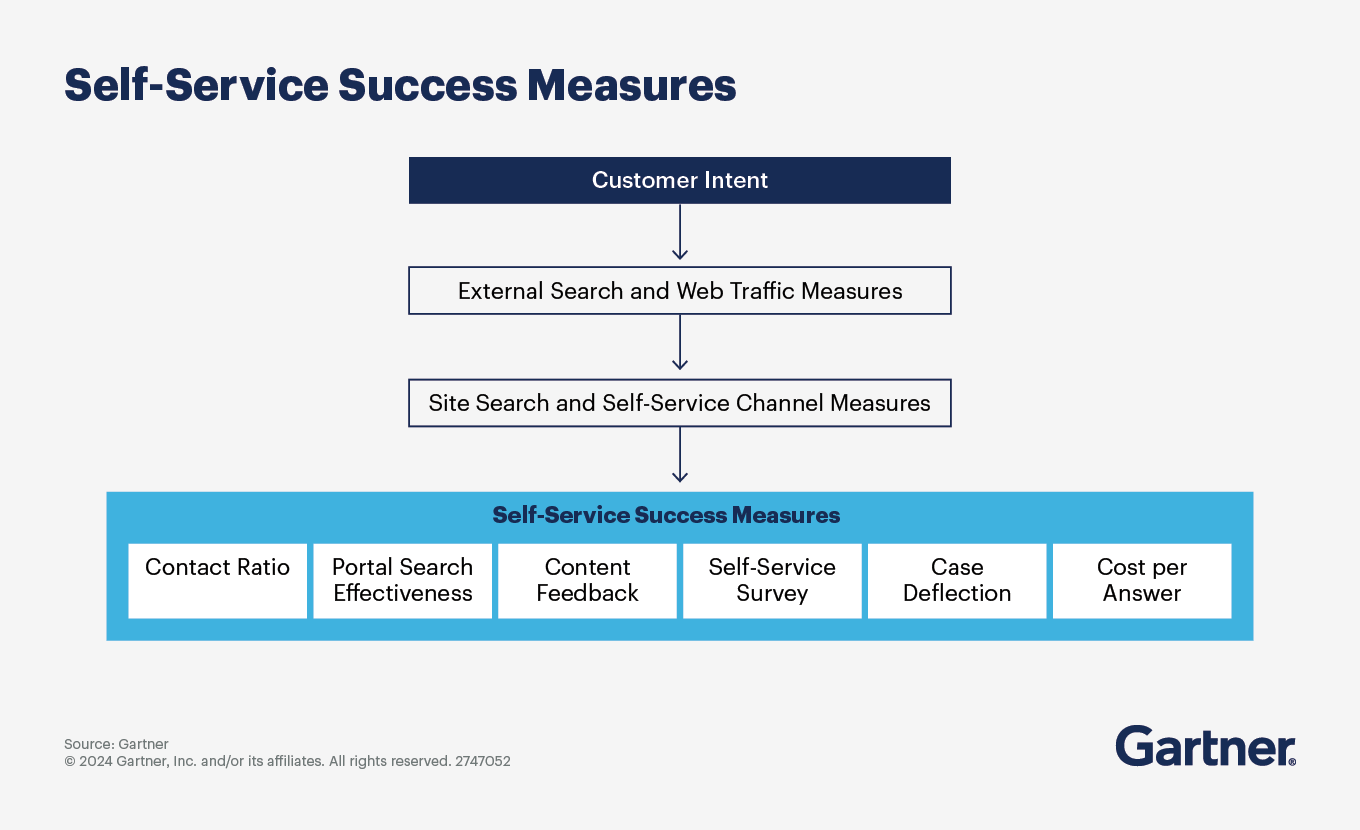
Use a range of metrics to broaden your view on your self-service effectiveness
Organizations that rely on customer survey data to assess self-service effectiveness have a limited perspective of the customer’s experience. Customer service and support leaders must use data from across the entire customer resolution journey for a more reliable assessment of self-service success.
To measure the success of your company’s self-service experiences, consider the following metrics:
Contact ratio. This metric measures the effectiveness of your self-service portal by looking at the ratio of web sessions to cases submitted online. It provides visibility into the foundational capabilities of your site and helps determine if there is enough content available to support self-service activity.
Portal search effectiveness. Measure the performance of your portal’s search engine. Collect usage data and analyze advanced search engine reports to see if users are finding, clicking on, reading and accessing content. This will give you insights into whether users are able to effectively search for and find the information they need.
Content feedback. Request feedback from customers on the content they interact with, such as knowledge base articles, product documentation and online learning courses. This will help you gauge the quality and usefulness of your self-service content.
Self-service survey. Ask customers for feedback during their self-service journey. Inquire about their satisfaction with the experience and whether they were successful in finding what they needed. While surveys alone may not provide a comprehensive view, they are still valuable in understanding customer perception.
Case deflection. Measure the percentage of customers who intended to contact customer support but were able to resolve their inquiry through self-service, without human intervention. This metric helps calculate savings and return on investment (ROI) for self-service.
Cost per resolution. Compare the cost of answering customer interactions through self-service versus assisted service. Self-service resolutions are typically more cost-effective. By comparing the cost per resolution for both methods, you can highlight the financial impact and ROI of a well-performing self-service portal.
By tracking these metrics, you can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the success of your self-service experiences and make informed decisions to improve them.
Attend a Conference
Join Gartner experts and your peers to accelerate growth
Gather alongside fellow leaders to gain insight on emerging trends, receive one-on-one guidance from Gartner experts and create a strategy to tackle your priorities head-on.
Gartner Customer Service & Support Conference
Denver, CO

Self-Service Customer Service FAQs
What is self-service customer service?
Self-service customer service allows customers to find answers and resolve issues on their own without direct assistance from a representative. This can include FAQ, knowledge bases, chatbots, virtual assistants, and online forums. Self-service customer service empowers customers to quickly access information and solutions 24/7, improving their experience and reducing the workload on support teams. Effective self customer service enhances efficiency and customer satisfaction, and reduces operational costs.
What are the benefits of self-service customer service?
Self-service customer service empowers customers to resolve issues quickly, enhancing satisfaction and convenience. It operates 24/7, providing immediate access to information. For businesses, it reduces the workload on self-service customer support teams, lowering operational costs. It allows staff to focus on complex issues, improving efficiency. Additionally, self-service customer supportleads to higher customer retention and loyalty, drives long-term success and provides valuable insights into customer needs and behavior.
What are the key capabilities of successful self-service?
Successful self-service requires:
User-friendly interface: Easy navigation and accessibility
Comprehensive knowledge base: Detailed FAQ, guides and articles
Effective search functionality: Quick and accurate information retrieval
Personalization: Tailored experiences based on user behavior
Integration with other systems: Seamless transitions to live support if needed
Analytics and reporting: Tracked usage and identified improvement areas
Continuous improvement: Regular updates based on feedback
Drive stronger performance on your mission-critical priorities.