D&A leaders can use the Master Data Management Maturity Model to assess capabilities, create a vision and roadmap a path to maturity.
- Gartner client? Log in for personalized search results.
Start by checking your maturity level
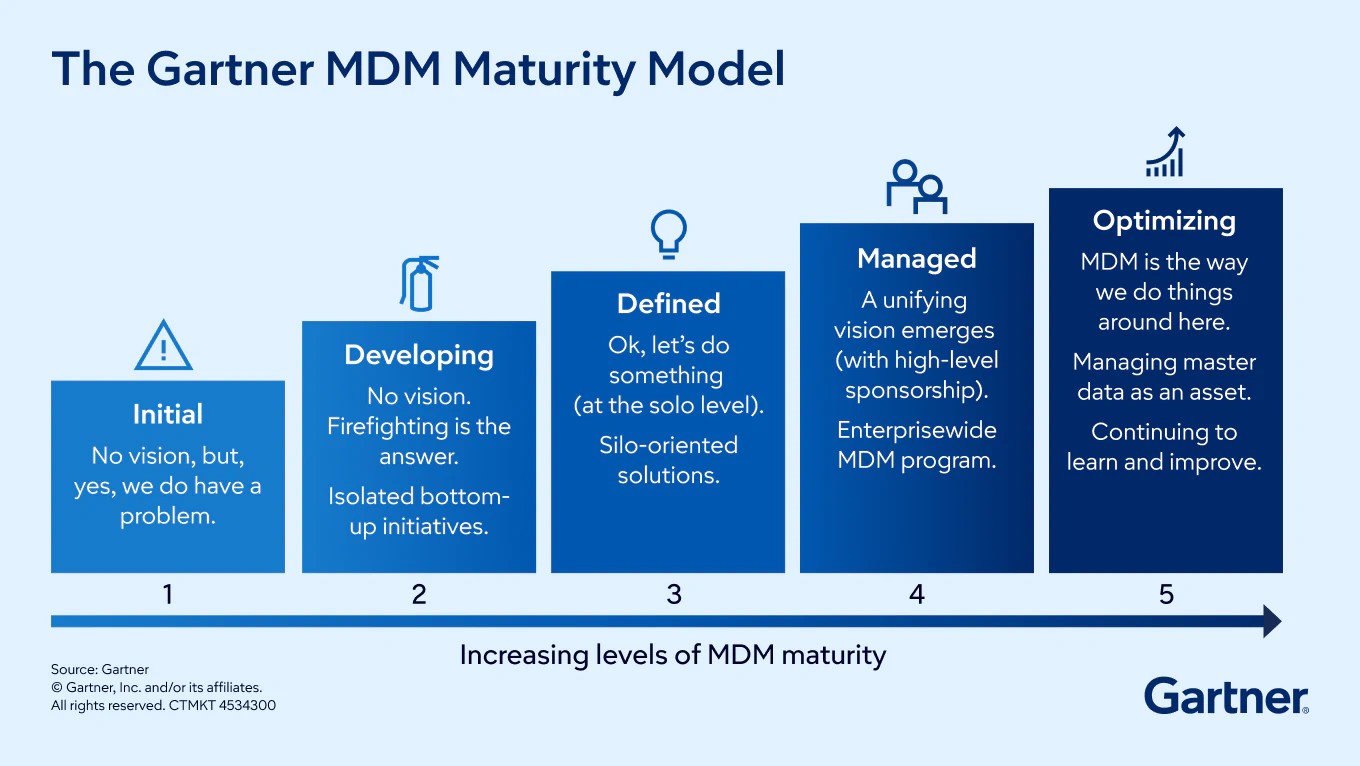
The Gartner Master Data Management (MDM) Maturity Model is essential for managing the health and direction of an MDM program. The first of five levels of maturity starts with awareness that master data problems are hampering the business’s effectiveness or ability to accomplish goals. Organizations at the highest level of maturity use and manage master data as a vital strategic asset, while making continuous improvements.
See Gartner research in action at our data and analytics conferences and events.
The first step is admitting you have a problem
Baseline your current maturity level to determine next best actions.
If you want digital business success and agility, you need MDM
Launching and managing a master data management initiative is demanding and complex, but is made increasingly urgent by digital business needs. It is also resource-intensive and disrupts IT and business practices, organizations and roles. Unfortunately, simply implementing MDM software will not fill the MDM gap. MDM programs are complex because master data touches so many critical business processes, applications and stakeholders.
For master data management programs to succeed, D&A leaders must develop organizational and workforce capabilities that not only sustain but strengthen them. D&A leaders who implement MDM should:
Select the level in the Gartner MDM Maturity Model that best characterizes their capabilities.
Use the maturity model with the Gartner MDM Operating Model to prioritize the capabilities needed to advance to the desired maturity level.
Refine the roadmap scope and deliverables by applying MDM capability assessments to the Gartner MDM Operating Model’s functional components.
Step 1: Assess MDM maturity
D&A leaders use the Gartner MDM Maturity Model to manage the health, strength and direction of their MDM program. The model breaks master data management maturity into five levels: initial, developing, defined, managed and optimizing. The exercise of assessing MDM maturity can motivate stakeholders to discuss what’s missing and brainstorm about the ideal future state.
Data domains, use cases and implementation styles vary depending on the needs of specific organizations and industries, so tailor the maturity model by integrating your organization’s range of requirements, master data management program scope, industry focus and vocabulary. Thousands of discussions with Gartner clients have revealed that most large organizations are at Level 2 (Developing) and working toward Level 3 (Defined). Some vertical industries like finance and healthcare tend to be more advanced because their data must adhere to strict regulation and control.
Step 2: Formulate your MDM vision
The more detailed the assessment, the better the roadmap you’ll be able to develop. Use the Gartner MDM Operating Model to add dimensions to your MDM maturity assessment. Combining the results of these two models clarifies the relative strengths and weaknesses of key MDM best practices. This critical assessment identifies components that are inhibiting progress across all program areas.
Use Gartner’s MDM Operating Model to inform a range of MDM activities:
Socializing and linking MDM concepts to outcomes and benefits for IT and business stakeholders
Assessing current MDM capabilities, comparing them with best practices, and evaluating the cost, risk or lost opportunities of maintaining the current situation
Envisioning the organization’s future-state MDM capabilities and conducting a gap analysis
Discussing stepwise improvements to the organization’s MDM capabilities (based on business benefit vs. time and cost to achieve)
Mapping MDM program phases and what must be done in various areas (e.g., governance, organization, metrics and infrastructure) to ensure success
Step. 3: Build your roadmap
Avoid stumbling blocks by planning for them. Assess the master data management capability of each functional component of the Gartner MDM Operating Model to refine the scope of the roadmap and deliverables.
Data and analytics strategy. From no strategy to MDM as a key enabler of business success
Scope. From no defined initiatives to enterprisewide with varying complexity levels
Metrics. From none to the basis of management and investment.
Governance. From nobody having responsibility to well-established cross-enterprise governance
Organization and roles. From silo-based applications or functions to continued efforts to optimize all master data management processes
Process. From silo-based applications or functions to continued efforts to optimize all master data management processes
Technology. From application-only data management to an enterprisewide, integrated and consistent set of capabilities
Master data management FAQs
What is master data?
Master data is the least number of consistent and uniform sets of identifiers and extended attributes that uniquely describe the core entities of an enterprise and are used across multiple business processes. This may include existing customers, prospective customers, citizens, suppliers, sites, hierarchies and the chart of accounts.
What is master data management?
Master data management (MDM) is a technology-enabled business discipline in which business and IT work together to ensure the uniformity, accuracy, stewardship, governance, semantic consistency and accountability of the enterprise’s official shared master data assets. Master data is the least number of consistent and uniform sets of identifiers and extended attributes that describe the core entities of an enterprise.
Attend a Conference
Experience Data and Analytics conferences
With exclusive insights from Gartner experts on the latest trends, sessions curated for your role and unmatched peer networking, Gartner conferences help you accelerate your priorities.
Gartner Data & Analytics Summit
Orlando, FL

Drive stronger performance on your mission-critical priorities.