Get the executive’s guide to understanding GenAI trends and technologies, piloting GenAI initiatives and scoping what lies ahead. Or scroll down to access GenAI insights for specific functional leaders.
- Gartner client? Log in for personalized search results.
What Generative AI Means for Business
Focus on GenAI initiatives that are both feasible and valuable
In an early-2024 Gartner poll, 40% of respondents said GenAI has been deployed in more than three business units.
Customer service and marketing are the primary business functions using GenAI.
Download this GenAI strategy workbook to ensure productive GenAI conversations in your function and business and to help you ask and verify:
- Why you are pursuing AI — and generative AI specifically
- What value it will bring
- How you will capture that value
- Which use cases to pursue
Download your copy by completing the form. This workbook is also available in French, German, Portuguese and Spanish.
Learn the GenAI landscape to fuel pilots and bigger successes later
Understand where GenAI stands and where the technology is going to maximize business impact.
- GenAI Trends and Hype
- How to Pilot GenAI
- GenAI Technologies
Trends in GenAI can help you pick your solutions
Generative AI can learn from existing artifacts to generate new, realistic artifacts (at scale) that reflect the characteristics of the training data but don’t repeat it. It can produce a variety of novel content, such as images, video, music, speech, text, software code and product designs.
To identify the opportunities of GenAI, savvy organizations are creating ongoing self-service and AI literacy programs to build awareness, increase knowledge and build a dynamic, iterative process for collecting ideas and use cases in a methodical manner.
Targeted multidisciplinary teams then use frameworks (such as the Gartner AI Opportunity Radar) to vet and juxtapose ideas based on business value and feasibility.
For stronger, faster AI outcomes, use Gartner’s proprietary AI Use Case Insights tool to explore, evaluate and prioritize over 500 proven AI use cases tailored to your industry.
Business units and functions are increasingly embracing GenAI
A January 2024 Gartner poll confirms the interest in GenAI remains strong:
- Nearly two-thirds of organizations are using GenAI across multiple business units.
- That’s a 19-percentage-point jump since September 2023.
- Forty percent of respondents say their organization has deployed GenAI in more than three business units.
- One in five organizations now has generative AI solutions in production.
- The primary business functions that have adopted or intended to invest in some form of GenAI solution are:
- Customer service (16%)
- Marketing (14%)
- Sales (12%)
- The IT function primarily focuses GenAI deployment on the software development life cycle, and infrastructure and operations.
Analyze GenAI pros, cons and business value
Understanding the benefits and risks of GenAI is important as you identify where and how it fits into existing and future business and operating models — and whether and how to experiment productively with use cases.
What are the benefits and applications of GenAI?
The benefits of generative AI include faster product development, enhanced customer experience and improved employee productivity, but the specifics depend on the use case. High-level, practical applications include:
- Written content augmentation and creation
- Question answering and discovery
- Tone
- Summarization
- Simplification
- Classification of content for specific use cases
- Chatbot performance improvement
- Software coding
- Product formulation
- Process improvements
- Analytics assistance
- Personalized recommendations
What are the risks of generative AI?
Oversight risks to monitor include:
- Lack of transparency
- Accuracy
- Hallucinations
- Bias
- Inadvertently exposing intellectual property (IP) and violating copyright
- Cyber and fraud attacks
- Negative impact on sustainability goals
How do you assess GenAI business value?
Be realistic about time-to-value. Three categories of GenAI initiatives deliver ROI in three different time frames:
- Quick wins, which focus on potential productivity improvements, pay off in less than a year.
- Differentiating GenAI drives competitive advantage with time-to-value between one and two years.
- Transformative GenAI initiatives can upend business models and markets. They tend to rely on a combination of AI techniques and often include multimodal GenAI. Because they are more complex, it usually takes more than two years to see real results.
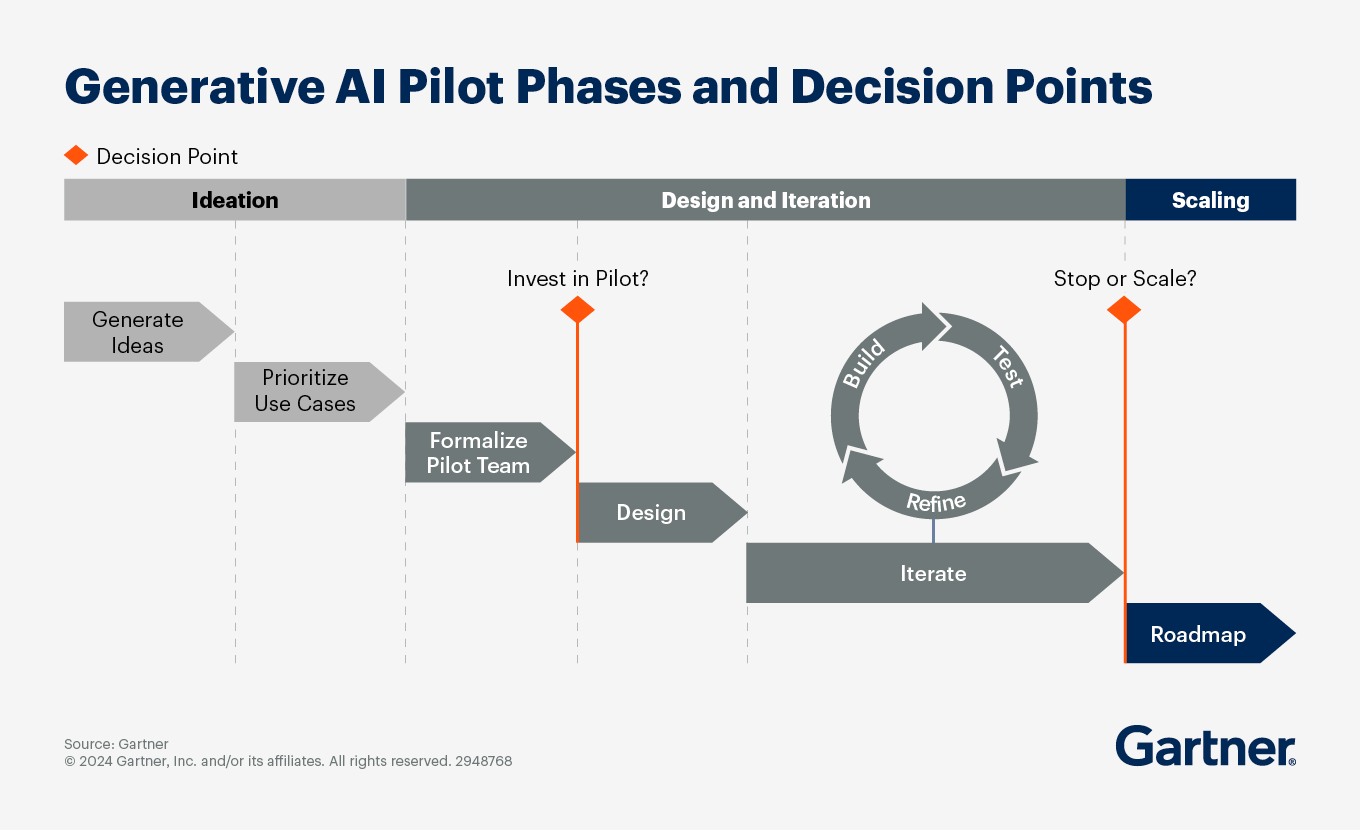
Why and how to plan and run GenAI pilots
Generative AI can be overwhelming. The opportunities are numerous but so are the different approaches to implementing this wide range of use cases, from buying an external application and customizing foundation models, all the way to building your own AI models from scratch.
Given this complexity, make sure your GenAI pilots — whether you are an IT leader or a business stakeholder — include these five steps:
- Generate use-case ideas with both business and IT involved, focusing on the disruptive potential of generative AI and the way in which it can enable strategic objectives.
- Prioritize the use cases for your pilot against their potential business value and feasibility. Focus on no more than a few use cases at stage.
- Install a “fusion team” — a small but diverse team, including business partners, software developers and AI experts to shepherd the pilot start to finish.
- Design and plan the pilot, aiming for a minimum viable product (MVP) to validate your hypothesis of the value that it could create for customers or employees. Define deployment approaches and risk mitigation measures required to quickly test whether you can capture specific improvements in target business KPIs.
- Deliver and iterate. Deliver the minimum functionality required to test the use cases and refine your assumptions on the cost and value of scaling them. Decide whether to stop, refine or scale each use case. Build on initial successes to expand your generative AI pilot.
What are the major GenAI technologies and how mature are they?
Generative AI uses a number of techniques that continue to emerge and evolve at an unprecedented pace.
Foremost are AI foundation models, which are trained on a broad set of unlabeled data that can be used for different tasks, with additional fine-tuning. Complex math and enormous computing power are required to create these trained models, but they are, in essence, prediction algorithms. (Also see: Gartner Experts Answer the Top Generative AI Questions for Your Enterprise.)
Since the late-2022 launch of ChatGPT, a chatbot capable of very human-seeming interactions, GenAI investment has ballooned. The market for GenAI-enabled virtual assistants and bots now includes many players. However, many GenAI technologies had already found their way to the Peak of Inflated Expectations on the 2023 Gartner Hype Cycle™ for Generative AI.
In this environment, business leaders risk overestimating the impact and underestimating the complexity of GenAI. Gartner nevertheless expects expanded adoption and predicts:
- By 2026, 75% of businesses will use generative AI to create synthetic customer data, up from less than 5% in 2023.
- By 2027, more than 50% of GenAI models used by enterprises will be specific to their industry or business function, up from about 1% in 2023. (These domain-specific models are much smaller than the massive GenAI models like GPT-4, and most will be built on top of AI foundation models.)
- By 2027, more than half of the selection of development assets from technology marketplaces will be performed by generative AI orchestration.
- By 2028, one-third of interactions with GenAI services will invoke action models and autonomous agents for task completion.
- By 2028, 30% of GenAI implementations will be optimized using energy-conserving computational methods, driven by sustainability initiatives.
Open-source models are rising in prominence and aggressively competing against closed-source ones. With AI-related regulations increasing, customers may favor open-source models, which have better deployment flexibility and customizability, and enable better control over security and privacy.
Artificial general intelligence looms in the distance
Artificial general intelligence (AGI) is one highly transformational (but currently hypothetical) and contentious element of the future of generative AI.
AGI, also called “strong AI,” can (theoretically) match or exceed human intelligence and solve problems never encountered during training. The Gartner Hype Cycle puts mainstream AGI adoption more than 10 years into the future — but short of a significant breakthrough, this could take decades or even centuries. Still, its benefits are potentially life-altering. AGI also raises considerable concerns among many stakeholders, however, stoking fears and unrealistic expectations about current AI’s true capabilities.
While AI already displays sometimes surprising emergent behaviors that humans did not program, it’s important for business leaders to avoid prematurely anthropomorphizing AI.
Still, AGI anticipation is accelerating the emergence of AI regulations and affects people’s trust and willingness to apply AI today. In the long term, AI continues to grow in power and, with or without AGI, will increasingly impact organizations, including the advent of machine customers and autonomous business.
Resources for the future of GenAI
These thought-provoking videos featuring Gartner experts explore where generative AI is headed:
Why Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) Matters — and Why It Doesn’t
2 Key Tactics for Generative AI and Beyond
AI in 2024: Implementation, Productivity and Regulation
How AI Unlocks Human Potential
Harness the Power of Democratized Generative AI to Transform Your Business
Get the generative AI guidance your functions and teams need
Attend a Conference
Accelerate growth with Gartner conferences
Gain exclusive insights on the latest trends, receive one-on-one guidance from a Gartner expert, network with a community of your peers and leave ready to tackle your mission-critical priorities.

Drive stronger performance on your mission-critical priorities.