How to implement AI agents to transform business models.
- Gartner client? Log in for personalized search results.
AI agents can help drive business model innovation
Generative AI (GenAI) has dominated attention with its rapid rise, but AI agents are increasingly emerging as the next major advancement in AI. These agents are starting to appear within enterprise software and are designed to support routine decision-making by operating autonomously inside defined workflows.
Pinpoint high-impact AI opportunities with Gartner’s AI Use Case Insights for IT Leaders. Discover, evaluate, and prioritize AI opportunities to accelerate IT transformation and demonstrate value to the business.
Think critically about integrating AI agents into the business strategy
Digital leaders cannot afford to overlook the potential business opportunities created by AI agents. However, implementing this technology requires careful consideration of all the potential applications, risks and solutions.
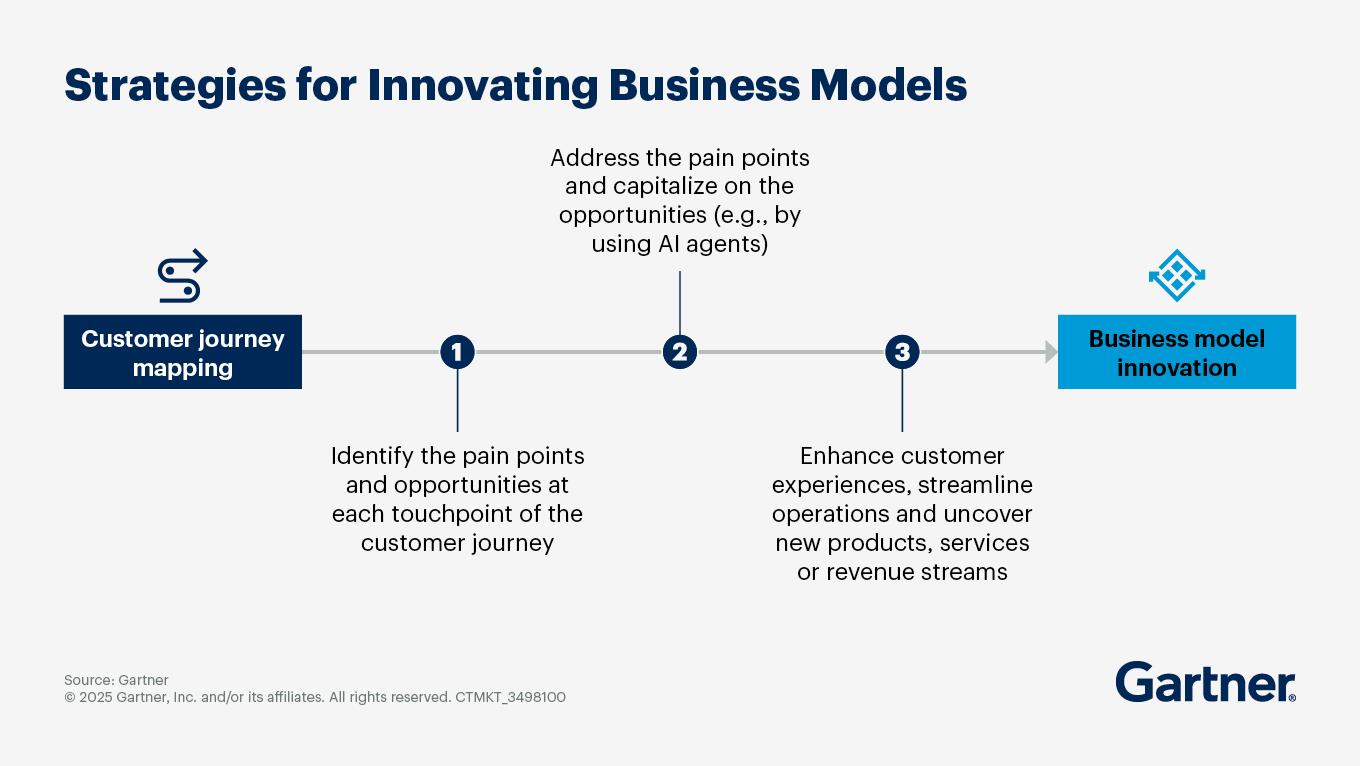
Innovate business models with customer journey mapping
In a market with fierce competition and rapidly emerging technologies — each with their own risks and benefits — digital leaders are under constant pressure to adjust and adapt the business model.
Business model innovation aims to discover new ways to meet customer needs, differentiate from competitors and increase efficiency and profitability by optimizing or transforming the existing business model.
Organizations looking to innovate their business models should consider leveraging customer journey mapping. By addressing specific pain points along this journey, they can enhance the experience for customers, streamline operations and uncover new products, services or revenue streams. AI agents can be a key solution for organizations looking to mitigate customer pain points and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Identify business opportunities for AI-agent-powered innovation
Digital leaders embarking on a journey to capitalize on AI agents should consider six key steps to identify and seize opportunities:
Define your goals. Figure out what the organization needs to achieve with the business model innovation.
Map the customer journey and touchpoints. Study how customers interact with the business. Map out their journey and identify key touchpoints.
Identify the pain points to uncover opportunities. At each touchpoint, flag pain points for improvements or increased efficiency.
Explore solutions with AI agents. Think about what innovative solutions AI agents could offer to address those pain points and seize opportunities.
Manage the change. Implementing new AI solutions means change. Strategize on the best way to manage this transition smoothly.
Evaluate the outcomes. Assess the impact of the AI-agent-powered innovations. Track KPIs and evaluate how well these AI solutions are meeting initial goals. Refine the strategies based on this data.
Explore all the AI-agent solutions
AI agents are not a one-size-fits-all solution and come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Organizations should carefully consider each AI-agent solution and select the technology that makes the most sense for their organization and application.
Types: There are six types of AI agents: reflex agents, goal-based agents, learning-based agents, utility-based agents, hierarchical agents and collaborative agents. Each type is suited to different scenarios and applications.
Applications: AI agents are ideal for a variety of situations that require automation, decision making and intelligent interaction with the environment.
Interaction models: AI agents can function with different levels of human involvement, such as human-in-the-loop versus human-out-of-the-loop.
Multiagent systems: Multiple agents can address complex tasks that individual agents cannot, resulting in more adaptable, scalable and robust solutions.
Embedded AI techniques: AI agents use AI techniques to sense, navigate and adapt to their environment. Techniques include optimization, natural language processing, and knowledge representation.
Risks: These agents are designed to act autonomously and proactively within an environment, often learning and adapting as they operate.
Implement LLM-based AI agents
Organizations looking for AI agents that are focused on planning, reasoning and processing should consider those that use large language models (LLMs) to drive execution of tasks and processes. LLM-based AI agents can provide a useful and accessible alternative to more established types of AI agents.
LLM-based AI agents use both programmed and prompted behaviors that require careful design, evaluation and monitoring to ensure the desired outcome. These agents should be built using a modular and composable approach to the software architecture.
Are you a CIO or IT leader at a midsize enterprise?
See how your peers are navigating AI adoption, vendor decisions and evolving business demands — with tools tailored to your role:
Explore our resources for midsize enterprises
Check out a curated list of Gartner’s most popular research being utilized by your peers
FAQs on AI agents
What are AI agents?
AI agents are autonomous or semiautonomous software entities that use AI techniques to perceive, make decisions, take actions and achieve goals in their digital or physical environments.
How can digital leaders innovate business models using AI agents?
Business model innovation involves optimizing or transforming existing business models to fundamentally alter how a company creates, delivers and captures value.
What are the types of AI agents?
There are six types of AI agents: reflex agents, goal-based agents, learning-based agents, utility-based agents, hierarchical agents and collaborative agents. Each type is suited to different scenarios and applications.
Attend a Conference
Experience Information Technology conferences
With exclusive insights from Gartner experts on the latest trends, sessions curated for your role and unmatched peer networking, Gartner conferences help you accelerate your priorities.
Gartner Data & Analytics Summit
Orlando, FL

Drive stronger performance on your mission-critical priorities.