- What are the key emerging technologies for 2026, and how should I use them?
- What is the future of AI? Is it AGI, superintelligence or something else?
- What is the Gartner Agentic Compass covered in the Gartner IT Symposium/Xpo™ conference keynote?
- What is so important about emotion AI?
- What is the disruptive potential of intelligent simulation, and what should be considered when implementing it?
- How will AI and robots transform or replace existing jobs?
- What is spatial computing, and what are its potential use cases?
- How will reasoning models evolve and transform AI adoption?
- Gartner client? Log in for personalized search results.
Emerging Technology Watch
Trending Questions on AI and Emerging Technologies
Gartner experts share quick answers to recently asked client questions on emerging technologies.
Last Updated January 2026
Table of Contents
- What is artificial general intelligence (AGI) and should I start to prepare for it now?
- What is Manus AI? Can it be used for business applications?
- What are small language models? And how do SLMs compare with LLMs?
- How is AI changing the landscape for edge devices?
- What is Deepseek R1 and why is it so innovative?
- How do domain-specific AI models differ from generic LLMs for enterprises?
- What is model context protocol (MCP) and how does it enable AI agents?
What are the key emerging technologies for 2026, and how should I use them?
By David Sugden
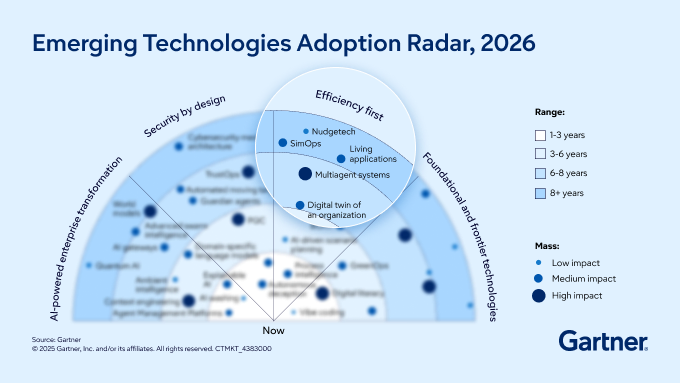
The 2026 Gartner Emerging Technologies Adoption Radar highlights four themes shaping the future:
AI-powered enterprise transformation
Security by design
Efficiency first
Foundational and frontier technologies.
Expect rapid advances in generative and agentic AI, explainable AI, and domain-specific language models to drive business transformation and customer experience. At the same time, organizations are embedding cybersecurity by default, leveraging innovations like secure access service edge (SASE), zero trust and AI-native security controls. Efficiency gains will come from the convergence of AI, automation, process intelligence and digital twins, enabling self-managing systems and real-time decision making. Foundational investments in cloud modernization, digital sovereignty infrastructure and next-generation platforms will underpin scalable, future-ready operations.
To make the most of these technologies, prioritize tangible outcomes, such as productivity and customer experience, by integrating AI and automation into core processes while establishing centralized governance for security and compliance. Adopt a strategic, risk-aware approach: Start with technologies that align with your business goals and readiness and continuously assess new innovations for their relevance and impact. This helps balance innovation with risk, ensuring your technology roadmap delivers measurable value in a fast-evolving digital landscape.
November 2025
What is the future of AI? Is it AGI, superintelligence or something else?
By Frank Buytendijk and Pieter den Hamer
Gartner predicts that AGI (artificial general intelligence) will not materialize for at least a decade, likely requiring several breakthroughs beyond scaling current technologies. By 2035, there will be progress toward AGI, but it will not be widely recognized as achieved.
AGI will only be achieved if AI technology matches the skills of all people on all cognitive tasks. Some technology providers are already openly discussing artificial superintelligence (ASI), AI that far surpasses human capability on all cognitive tasks. Because AGI and ASI require different approaches, they are almost parallel development paths.
Gartner believes both AGI and ASI have significant challenges and should be avoided. AGI performance is directed compared with people, whose ultimate goal it is to replace. Superintelligence, far surpassing human capability, can become problematic when in the wrong hands or be a single point of failure.
As such, we propose a third approach to general intelligence: augmented collective intelligence (ACI). Picture a swarm of connected and dedicated agents, combining different styles of AI, working side by side with people who contribute human intelligence. General intelligence emerges from this network. ACI best matches the goal of technology: to enhance human capability and improve quality of life.
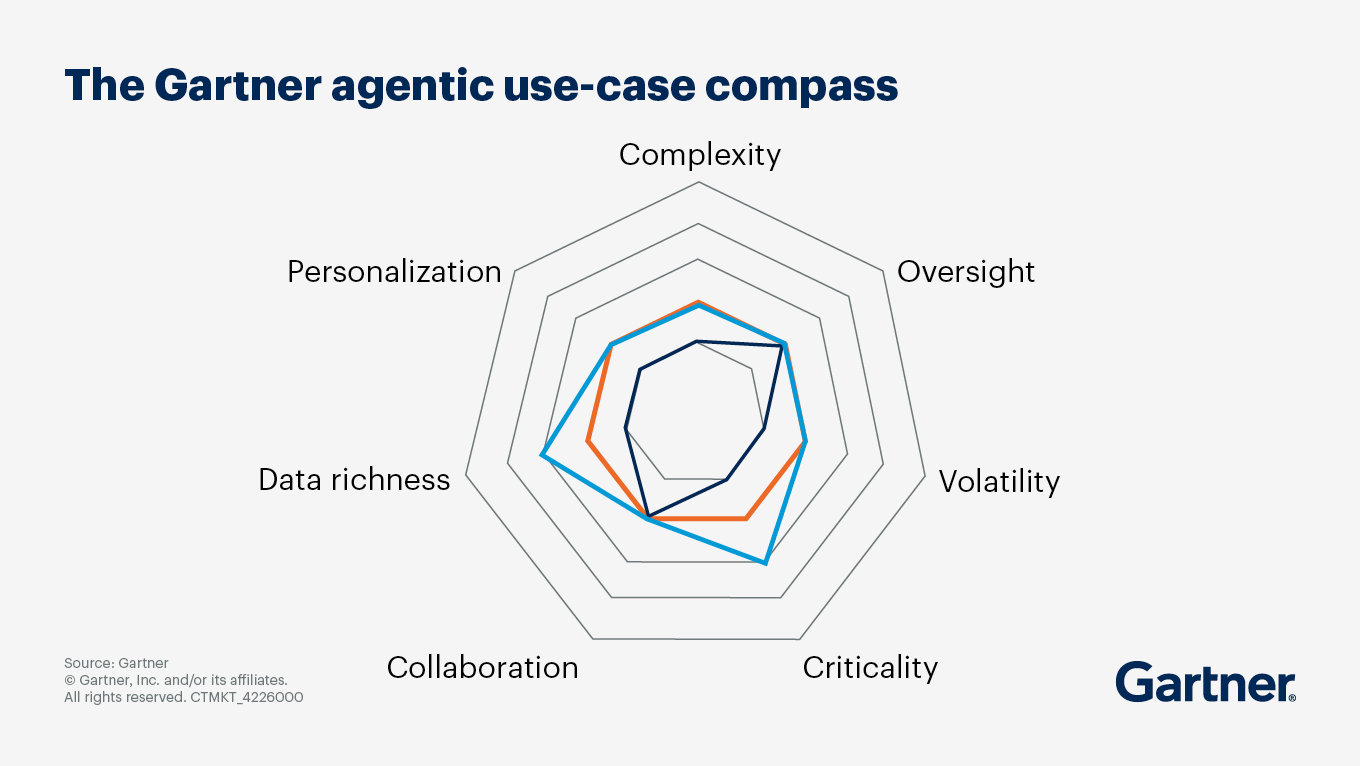
What is the Gartner Agentic Compass covered in the Gartner IT Symposium/Xpo™ conference keynote?
The Gartner Agentic Compass aligns organizational needs with agentic capabilities to help organizations navigate the increasingly complex landscape of agentic AI solutions. Its main objective is to enable enterprises to align their needs with appropriate AI capabilities, ultimately driving better business outcomes.
The Agentic Compass is composed of two frameworks — one for assessing use-case needs and the other for evaluating distinct agentic capabilities. Based on analysis of 169 providers and 200 real-world agent deployments, these frameworks offer a grounded reference for defining requirements, constraints and objectives. This enables better alignment with platforms, prebuilt agents, governance tools and optimal technology combinations across multiple vendors.
What is so important about emotion AI?
By Alizeh Khare
Emotion AI is a critical differentiator in the next wave of deployment of computer vision and robotology. To effectively leverage emotion AI to drive innovation while mitigating risks associated with its implementation, CIOs evaluating the technology (also known as affective computing) must consider the following:
Enhancement of customer engagement. Emotion AI can significantly improve human-machine interactions by analyzing emotional states (e.g., through voice and facial recognition) and enabling businesses to tailor responses that better resonate with customers.
Applications in other sectors. Emotion AI is used in healthcare for diagnostics and in marketing for neuromarketing strategies that gauge product reactions. Its ability to analyze emotional signals across multiple modalities allows businesses to refine their approaches and improve customer retention and satisfaction.
Privacy concerns. Current usage scenarios indicate a need to prioritize aggregated, context-based insights (e.g., “25% of customers showed frustration”) over individual emotion attribution to support regulatory compliance and build trust.
Bias and accuracy. Relying solely on expression detection is insufficient for understanding intent; multimodal systems that analyze multiple cues perform better. Clear metrics — such as precision, recall, fairness, false alarms, latency, user satisfaction and regulatory compliance — are essential, especially in areas with strict privacy laws.
Ethical oversight and transparency. Ensure that systems are transparent about how emotional data is used and prioritize ethical decision-making processes that avoid applications related to mass monitoring or surveillance.
Regulatory compliance. Safeguarding user privacy by using privacy-preserving machine learning (ML) techniques such as federated learning, on-device processing, confidential computing, explicit opt-in consent and explainable AI will continue to be a top priority.
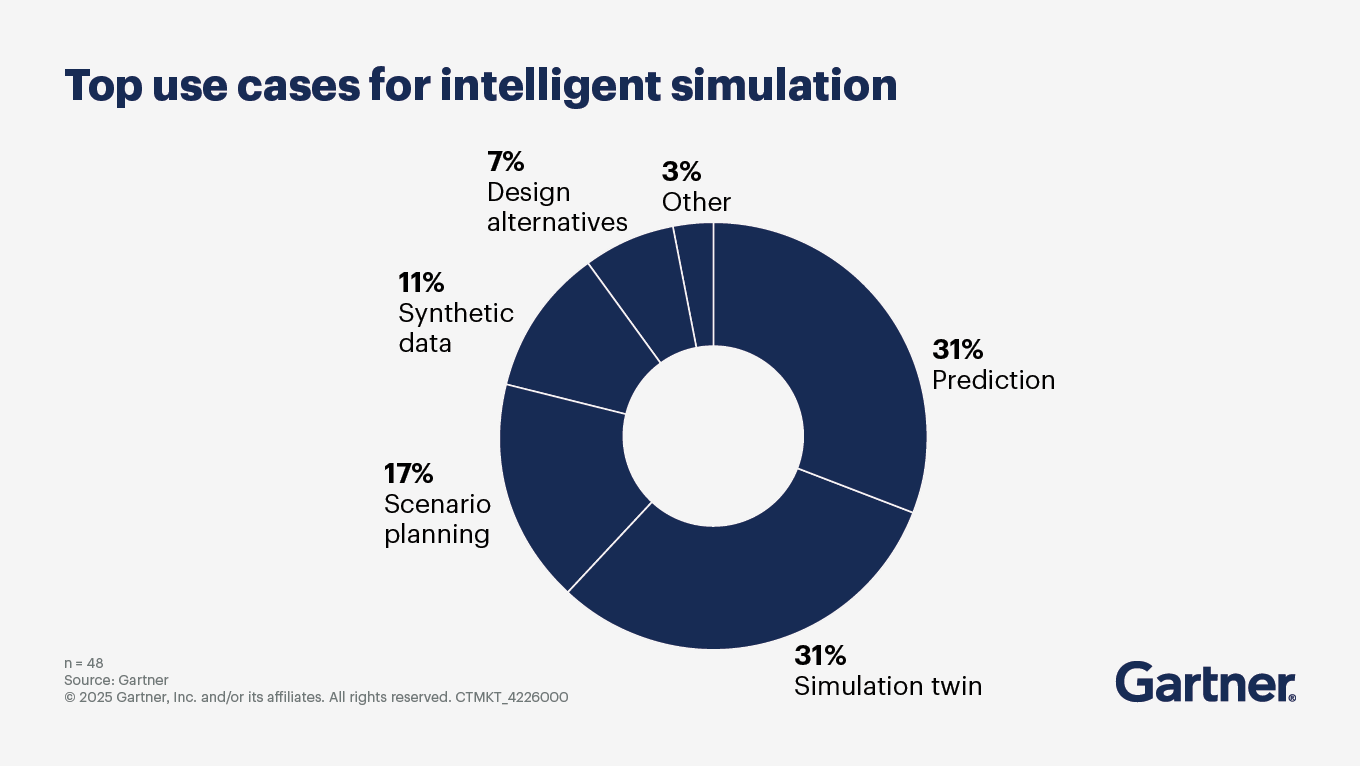
What is the disruptive potential of intelligent simulation, and what should be considered when implementing it?
Intelligent simulation is rapidly emerging as a transformative technology that integrates advanced simulation engines, digital twins, GenAI, synthetic data and quantum computing to deliver unprecedented scale, efficiency and accuracy in decision making. It is moving from a tool that offers guidance by driving innovation through generating, analyzing, and designing at scale, to one that can autonomously execute decisions based on simulated results. Its use cases are vast.
The following considerations, particularly in the context of digital marketing and broader business operations, are essential in implementing intelligent simulation solutions:
Alignment with business objectives. Ensure that intelligent simulation technologies address relevant challenges and enhance decision-making capabilities while aligning with marketing and operational goals.
Technology integration. Effective implementation relies on seamless integration with existing IT infrastructure, including enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and customer relationship management (CRM) tools. Prioritize platforms that can easily interface with current business solutions to maximize operational efficiency.
Data accessibility and quality. The success of intelligent simulation is heavily dependent on access to quality data. Focus on strategies that ensure data integration from various sources to facilitate accurate modeling and scenario analysis. Address potential data silos and ensure that data management practices support high-quality inputs for simulations to optimize their accuracy.
User experience and accessibility. Support the development of low-code or no-code interfaces that allow users to leverage intelligent simulation tools without needing extensive technical expertise. This will help democratize access to insights generated from simulations across the organization.
Cultural change management. Implement a change management strategy that engages stakeholders at all levels to ensure they understand the benefits of intelligent simulations and how these tools can enhance day-to-day operations.
Demonstrating value and ROI. Emphasize tangible business value outcomes such as improved efficiency, better decision making and enhanced customer insights.
A focus on predictive capabilities. Facilitate the development of models that not only provide real-time insights but also help anticipate future operational needs and market trends.
Continuous learning and adaptation. Intelligent simulation applications should be designed to learn from their execution context, allowing them to adapt over time. Ensure processes are in place for ongoing evaluation and refinement of simulation capabilities to keep pace with changing business environments and user needs
October 2025
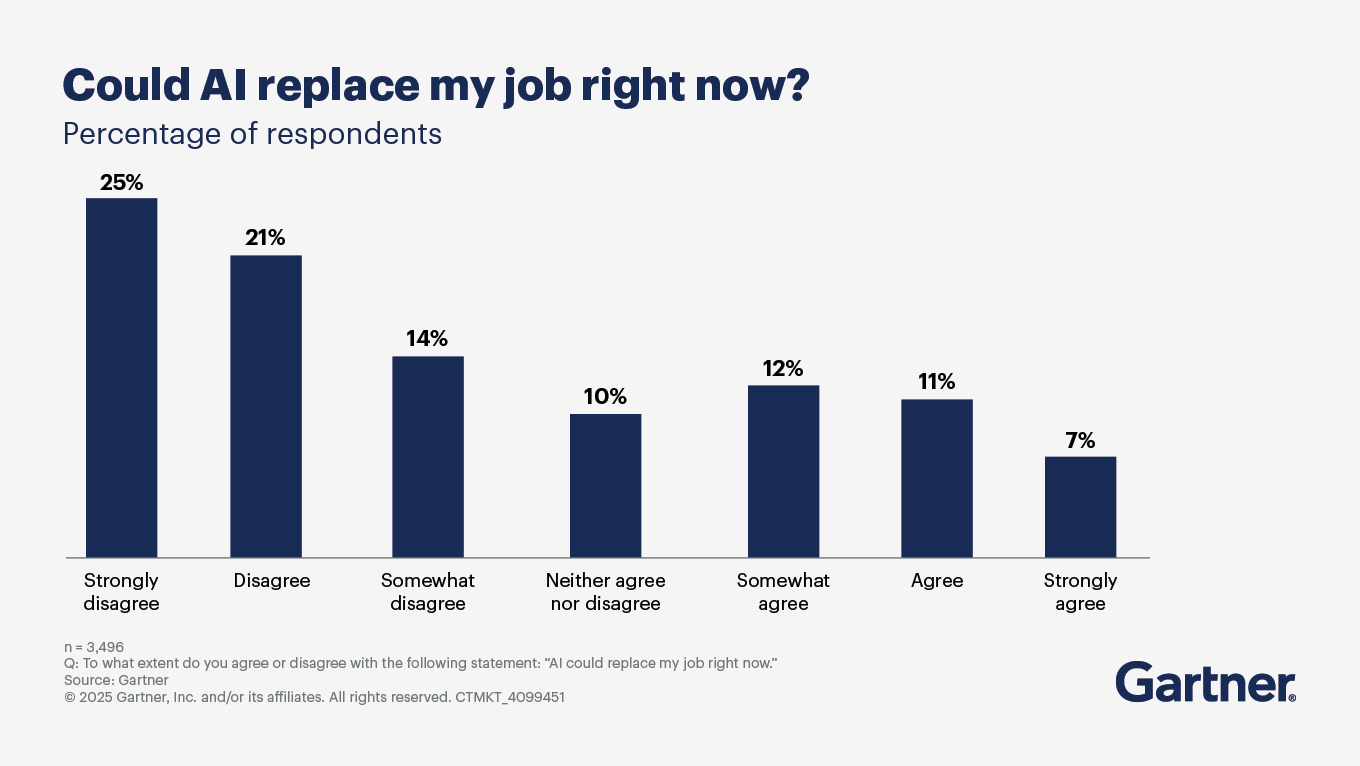
How will AI and robots transform or replace existing jobs?
In short, significantly. Gartner predicts that by 2030, 90% of humans will engage with smart robots on a daily basis, due to smart robot advancements in intelligence, social interactions and human augmentation capabilities, up from less than 10% today.
This transformation is characterized by several key trends:
Automation of routine tasks to allow human workers to focus on more complex and value-added activities.
Creation of new roles, like AI engineers, data scientists and AI ethicists. This indicates a transformation in job functions rather than outright job loss.
Enhanced decision-making, such as in customer service, for example, where AI can assist agents by providing real-time data and insights, thereby improving the quality of service.
Workforce augmentation, in part thanks to the rise of polyfunctional robots, which can perform multiple tasks and adapt to various environments. This shift not only transforms job roles but also enhances workplace safety and productivity.
Continuous operation through hot inspection and in-situ monitoring by smart robots, even in hazardous environments.
Physical agency of AI in agent networks, where robots act as the physical embodiment of AI agents — enabling digital intelligence to perceive, interact and act within the real world.
To prepare the workforce for new responsibilities, focus on reskilling, upskilling and carefully managing workforce transitions to mitigate fears and retain talent.
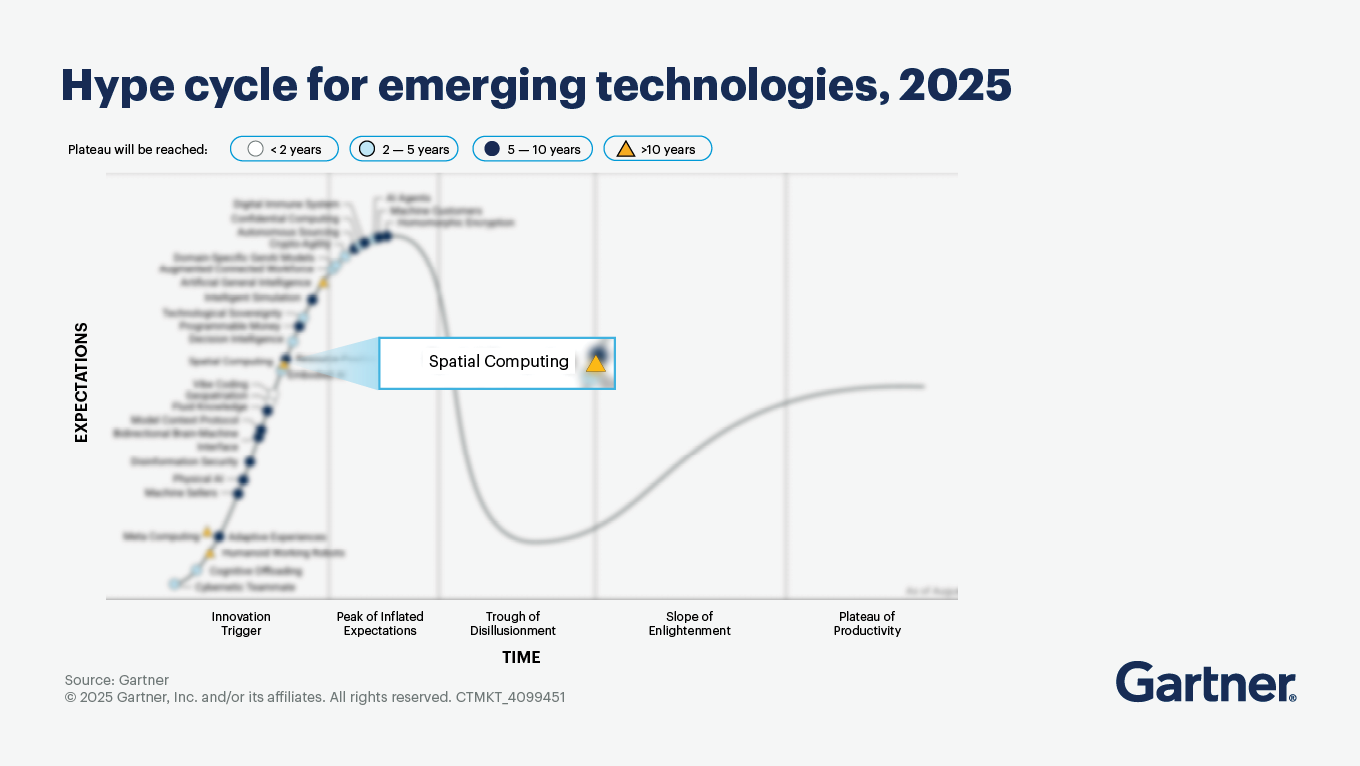
What is spatial computing, and what are its potential use cases?
By Tuong Nguyen
Spatial computing boosts human perception and thinking and improves machines’ ability to understand, move through and interact with real-world locations and objects. By organizing and linking digital content to the real world, this technology unlocks new avenues for business and dramatically improves the effectiveness of interactions between people, systems and their environments.
The market for spatial computing is expected to reach $1.7 trillion by 2033. Potential use cases include the following.
Embodied AI/physical AI uses a shared content source describing the state of and relationships between things to orchestrate and respond. For example, autonomous vehicles respond to first responder vehicles to request green lights, reroute cars and alert pedestrians through connected devices.
Agentic AI is a unifying framework to connect diverse devices and content across public and private data sources using an appropriate graph. For example, enabling AI agents controlling thermostats and those controlling energy-storage battery systems to work together to maximize comfort while saving money and cutting emissions across a neighborhood.
Spatial web is a physical world wide web that delivers just-in-time information and hyperpersonalized experiences and services via an internet of spaces and places for a variety of use cases, including retail, advertising, industrial maintenance and prototyping as well as orchestration and collaboration between AI agents.
As organizations explore these use cases, they must also address challenges such as data privacy, standardization and the integration of spatial computing into existing workflows.
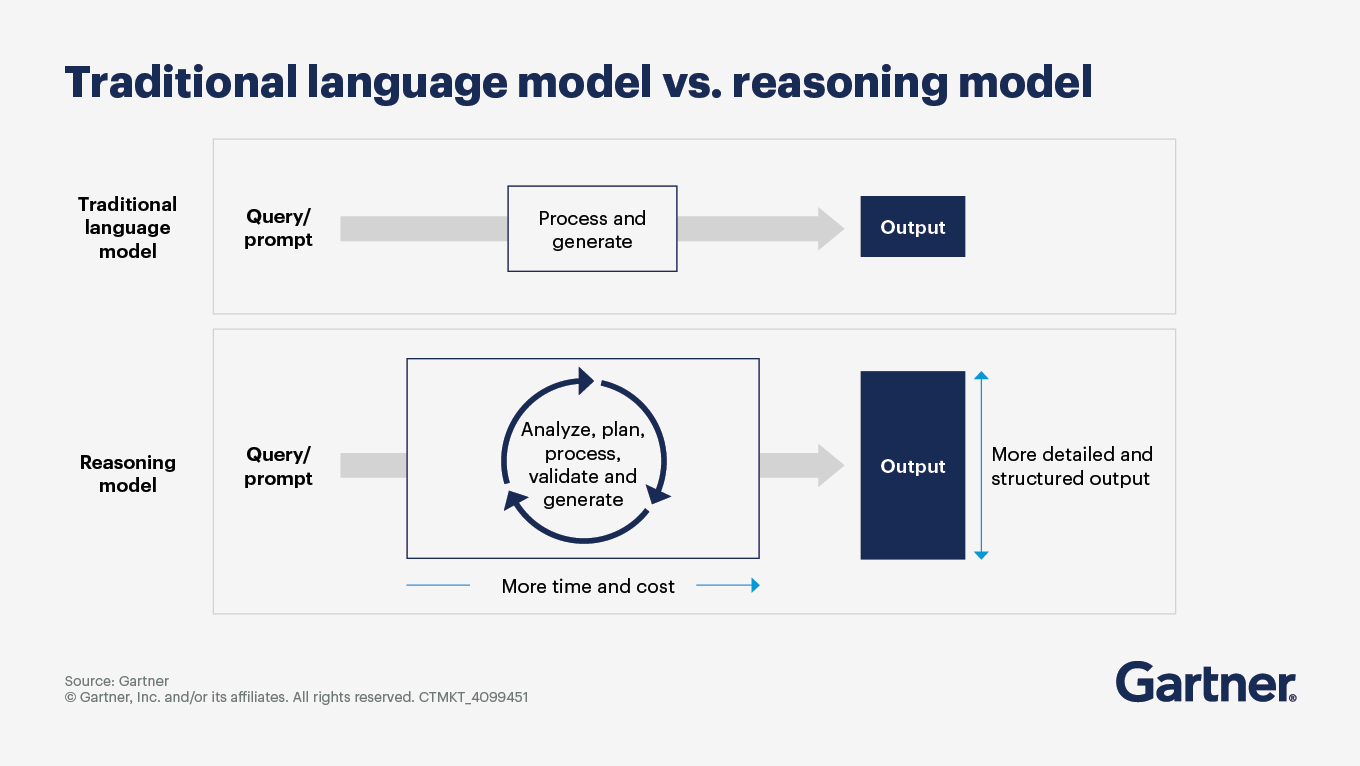
How will reasoning models evolve and transform AI adoption?
Reasoning models are expected to undergo significant evolution in logical inference, complex problem solving and multistep reasoning. These models will increasingly use chain-of-thought processes and self-reflection, allowing them to mimic human-like thought patterns more effectively than traditional models, which primarily rely on pattern recognition. This evolution is driven by advancements in reinforcement learning, where models are trained to validate their outputs in areas such as math, logic and coding.
Gartner projects that by 2029, investment in reasoning models will underpin the success of more than 70% of agentic AI applications, a significant increase from 0% in 2024.
The shift toward more sophisticated, domain-specific reasoning models will enable organizations to automate complex tasks, improve decision-making and redefine workforce dynamics, ultimately leading to a more integrated and efficient use of AI technologies in business operations. The anticipated growth in agentic AI applications underscores the importance of investing in these advanced reasoning capabilities to stay competitive in an increasingly AI-driven landscape.
To see previously featured answers to client questions on emerging technologies, visit the archive.