Prepare the finance function to maximize the potential benefits and mitigate the risks of agentic AI.
- Gartner client? Log in for personalized search results.
Agentic AI Will Transform Finance: Here’s What CFOs Should Do Now
By Marco Steecker | October 27, 2025
Agentic AI is not your everyday AI. CFOs need a proactive plan to manage it.
Breakthrough solutions like agentic AI are moving quickly into finance functions, with 57% of finance teams already implementing or planning to implement. Unlike robotic process automation (RPA), which requires explicit inputs and produces predetermined outputs, generative AI (GenAI), which responds to user-based prompts, and other conventional AI technologies that only follow established training, AI agents will be able to make decisions, solve problems and act autonomously. Although agentic AI is still in its early stages of development, CFOs should start preparing now to lay a foundation for future deployments and competitive advantage.
See Gartner insights in action at our finance conferences and events.
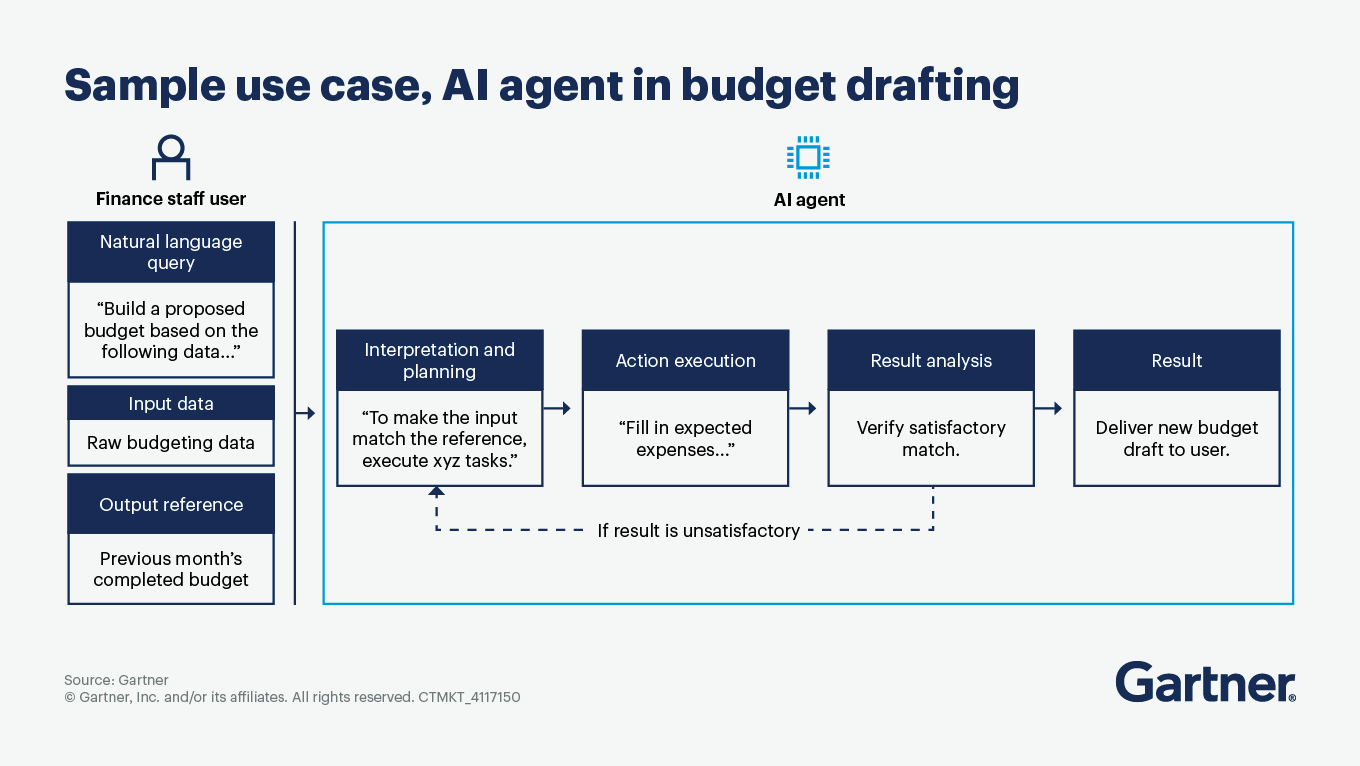
Take early action to set the stage for agentic AI in finance
The following steps will help maximize agentic AI’s impact on your finance function.
Get familiar with how to apply agentic AI in finance
Agentic AI combines three basic capabilities to perform tasks:
Action: In digital finance environments (such as ERPs, financial planning systems, close and consolidation tools, and databases), agentic AI detects discrepancies, matches transactions, standardizes entries and transforms data for analysis.
Cognition: Agentic AI builds a knowledge base and memory to make logical inferences.
Perception: Agentic AI “senses” changes in digital and physical environments by monitoring text, numbers, images and other data.
As you consider relevant use cases for your organization, look for workflows featuring:
High-volume interactions, transactions and context: Agentic AI uses these to build knowledge, act and track objectives (for example, journal entries, reconciliations versus few high-value contracts).
Mature data, metadata, APIs, workflows and process orchestration: Rich, well-structured financial data and high-quality forecasting and analytics models enable more detailed reporting.
Established authorizations, privacy, trust and security controls: Preexisting governance streamlines oversight and reduces hallucinations and other risks.
Experienced users of large language models (LLMs) and GenAI tools: Experienced users will find agentic AI interactions familiar, softening the learning curve.
Understand agentic AI’s limitations
Agentic AI can’t understand and do everything we ask of it. Like conventional AI tools, it has significant limitations, including:
Reliability: Agentic AI systems can hallucinate, get stuck in loops and fail unexpectedly.
Scope: AI agents operate best and risk is lower when they perform specific versus general-purpose tasks.
Memory: Adding to an AI agent’s memory can allow it to handle more decision-making complexity, but it can also lead to confusion and degrade performance.
Learning: Although AI agents can learn on their own, they learn faster and more accurately when humans provide feedback, update the agents’ memory in a structured way and correct mistakes as they happen. This also helps prevent AI agents from adopting incorrect processes.
Explainability: Although AI agents can provide explanations for their actions, the underlying AI models remain unpredictable and opaque. This makes it almost impossible to understand exactly how a specific input leads to a particular output.
Assess the vendor landscape for agentic AI in finance
Building AI agents is possible for finance organizations with the willingness and expertise, but only about 31% plan to develop AI agents in-house. The rest plan to activate agentic AI within existing platforms, buying new software or partnering with external consultants.
Major financial technology vendors are already rolling out agent-like features as add-ons, and RPA providers are also upgrading their offerings. To explore early adoption, proactively engage current vendors — but note that agentic AI features alone usually don’t justify replacing a major platform.
If your organization is already thinking about switching systems or adding new tools, check the maturity of vendors’ current offerings and their future roadmap. Assess the value of prebuilt solutions by asking the following:
How much extra investment is needed to activate agentic AI in my existing platforms?
Are the benefits worth the additional cost?
Does a potential vendor’s agentic AI features make their solutions better than competitors’?
Request demos and proof-of-concept discussions, and ask if the AI can choose its own actions, learn as it goes and handle unstructured data. Most current solutions fall short of being true AI agents, but testing the features is a good starting point.
Establish early agentic AI governance approaches
Agentic AI’s ability to solve complex finance problems autonomously is one of its key benefits. But without human oversight, an AI agent’s actions can be opaque, hard to audit and difficult to hold to account.
Set governance guardrails for agentic AI early — ideally as an extension of existing AI protocols — and include the following:
Preestablished approved use lists: Have subfunction leaders and process owners list which processes AI agents should or should not be allowed to perform, based on compliance risk and potential financial harm. Safer use cases include anomaly detection, error identification and internal reporting.
Human oversight and exit conditions: Have process owners review AI agent actions and establish early human-in-the-loop checks to provide context to the agent, approve or reject decisions and prevent risk. Exit conditions should be programmed to flag high-risk circumstances that require staff intervention or approval.
Multiagent teams: For complex tasks, require teams of specialized AI agents rather than a single “do it all” agent. This improves execution and allows for the embedding of validation or auditing agents, providing an additional layer of governance.
Agentic AI in finance FAQs
What is agentic AI in finance?
Agentic AI is an approach to building AI solutions that use one or more software entities (called AI agents) to understand circumstances, make decisions, take actions, and achieve goals in their online or real-world environments, either on their own or with human help. As agentic AI in finance matures, it will be able to automate highly complex finance tasks in complex digital environments, driving workflow efficiencies that current technologies can’t address.
Why should CFOs care about agentic AI in finance?
Agentic AI in finance has the potential to transform finance operations by performing a high volume of complex, judgment-based activities across multiple applications and stakeholders. While agentic AI is still in its early stages of development, CFOs should lay the groundwork for adopting agentic AI in finance by familiarizing themselves with its potential benefits and risks, governance approaches and implementation best practices.
Attend a Conference
Join Gartner experts and your peers to accelerate growth
Gather alongside your peers in National Harbor to gain insight on emerging trends, receive one-on-one guidance from a Gartner expert and create a strategy to tackle your priorities head-on.
Gartner Finance Symposium/Xpo™
National Harbor, MD

Drive stronger performance on your mission-critical priorities.