Gartner’s Supply Chain Top 25 identifies, celebrates and profiles global supply chain excellence.
- Gartner client? Log in for personalized search results.
The Gartner Supply Chain Top 25 for 2025

Discover the global supply chains that ranked highest for supply chain excellence
Superior supply chains don’t just push products; they deliver on the business’s purpose. The Gartner Supply Chain Top 25 is a renowned annual ranking of the world’s superior supply chains.
The 2025 eBook shares the list of the top global supply chains operating today based on business performance metrics and community opinion. Download the eBook for:
An up-close look at leading supply chains
Macro trends differentiating the leaders
Key initiatives to benchmark your supply chain transformation
3 success drivers among the Gartner Supply Chain Top 25 for 2025
Every year we research hundreds of supply chains to understand key priorities and investments. Three supply chain macro trends are accelerating capabilities at the best supply chain companies.
Autonomous Operations
Agentic AI
Water Stewardship
Autonomous operations help supply chain organizations create value and mitigate risk
In the rapidly evolving landscape of supply chain management, the distinction between mere automation and the transformative potential of autonomous operations is becoming increasingly pronounced. Unlike traditional automation, which focuses on isolated machines or processes, autonomous operations integrate a wide array of activities, significantly enhancing productivity across the supply chain. CEOs aren’t being hesitant when it comes to autonomous operations: According to the 2025 Gartner CEO and Senior Business Executive Survey, within 3 years we will see a shift to 100% automated systems and processes operated without human involvement across many areas:
- 38% of companies plan to use intelligent automation for logistics, distribution and or production;
- 33% want to do the same for contract management and payments; and
- 19% want to improve contract sales and negotiation using autonomous capabilities.
Autonomous operations represent a comprehensive advancement, encompassing multiple domains with capabilities such as self-monitoring, self-regulation and continuous optimization. This paradigm shift not only alleviates employees from repetitive tasks but also enhances workplace safety by minimizing human presence in hazardous environments.
By automating strategic decision making and execution processes, autonomous operations are recognized as both a substantial value creator and a risk mitigator, driving overall business performance. The application of autonomous operations spans diverse areas within the supply chain, including "lights off" production and warehousing, as well as "hands off" planning and customer services.
Companies are at various stages of this evolution, with the Gartner Supply Chain Top 25 leaders distinguished by several key capabilities:
A comprehensive digital transformation roadmap
The ability to sense conditions at machine, system and process levels
Utilization of platforms to process data, ensuring autonomous decisions do not adversely affect other functions
The capability to maintain process integrity amidst variability
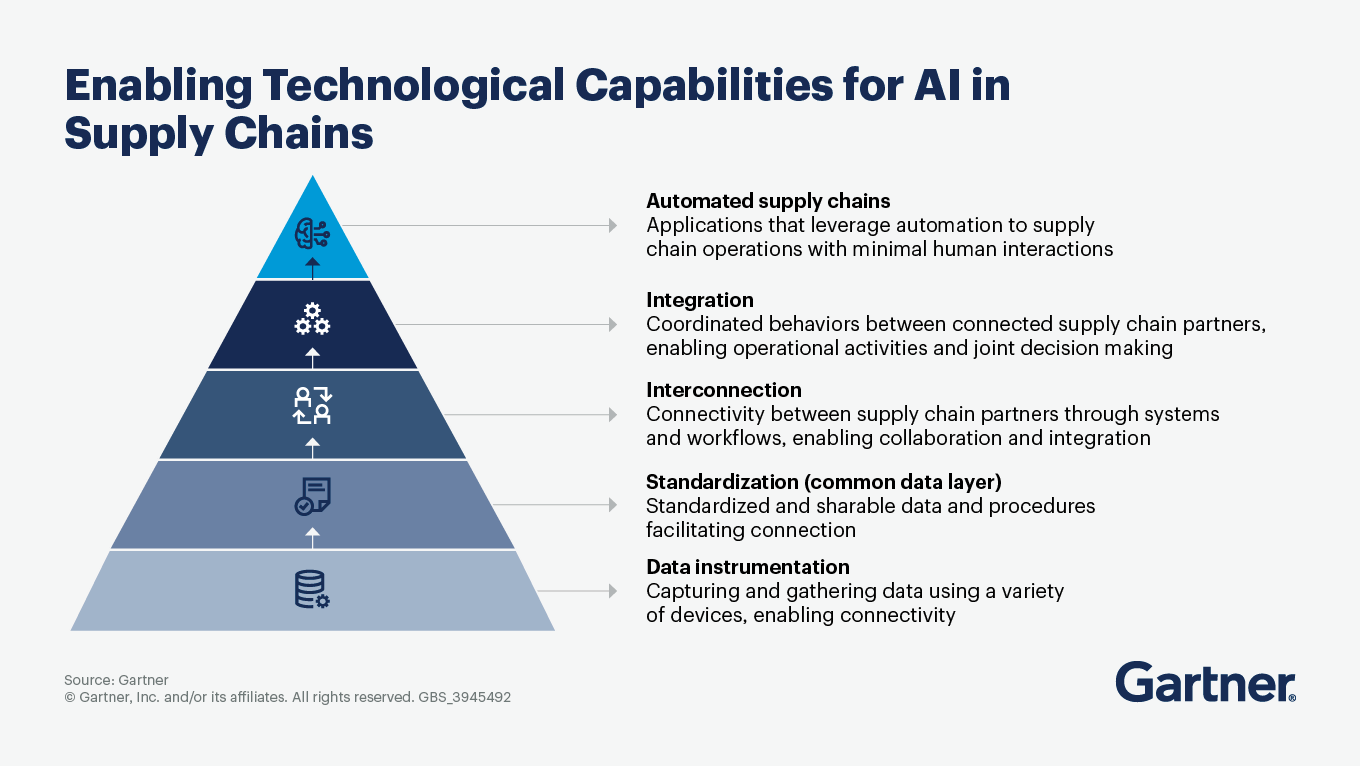
The holistic adoption of autonomous operations yields a positive ripple effect across organizations, enhancing everything from production to delivery. These operations apply to business processes that can autonomously make decisions, take actions and continuously learn to improve execution.
For supply chain leaders, developing a roadmap that integrates both physical process flow automation and decision automation is crucial. Autonomous operations enhance cross-functional processes, optimize network efficiency, and improve service delivery, thereby boosting financial, employee and customer value.
Financial value is enhanced by mitigating risks and reducing costs.
Employee value is improved by reducing repetitive tasks and enhancing safety, particularly in high-risk areas or during antisocial hours.
Customer value is elevated through reduced process variability, leading to better product quality and lower operational costs.
Agentic AI introduces a new dimension of supply chain transformation
As organizations continue to embrace the transformative potential of AI on the future supply chain, the next frontier of innovation is emerging in the form of agentic AI. Agentic AI introduces a new dimension of intelligence and adaptability. Unlike generative AI, which focuses on creating content like text or images from large datasets, agentic AI extends these capabilities by autonomously making decisions and executing actions to achieve its goals without constant human intervention. By integrating the creative aspects of generative AI with the problem-solving approaches of traditional AI, agentic AI is equipped to conduct complex tasks in dynamic environments, promising to deliver autonomous supply chain decision making and execution.
Many of the companies in this year’s Gartner Supply Chain Top 25 are leading the charge in adopting agentic AI, moving beyond traditional AI approaches that rely heavily on explicit human instructions. Agentic AI harnesses the capabilities of advanced machine learning, deep learning and reinforcement learning to autonomously learn from data, adapt to new information and interact dynamically with its environment. This groundbreaking advancement is distinguished by its "agency," allowing AI systems to act independently, make decisions and pursue goals based on environmental understanding. Building on the foundations of generative and traditional AI, agentic AI represents a significant evolution in the field of supply chain AI.
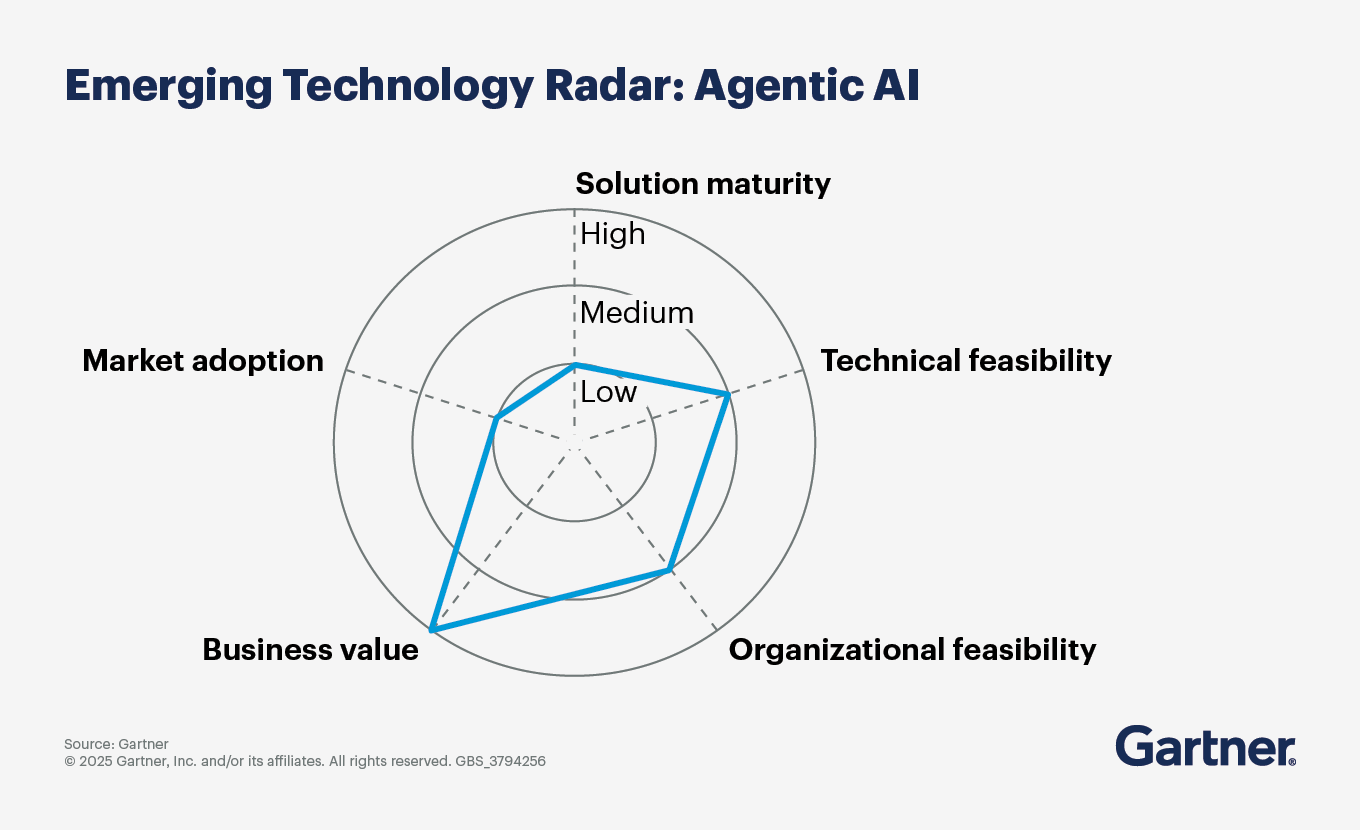
Agentic AI can be deployed across supply chain functions to support real-time sensing, decision making and execution. Some examples include:
Agentic dynamic demand forecasting: Agentic AI breaks down forecasting into data collection, pattern recognition and predictive modeling. It autonomously sources data, identifies new patterns and updates forecasts in real-time, dynamically optimizing inventory levels and placing orders without human intervention. This adaptability allows it to continuously refine demand forecasts and inventory decisions.
Agentic supplier selection: Agentic AI evaluates and updates suppliers based on performance metrics, cost analysis and reliability scores. It tracks market conditions and geopolitical factors affecting supply chain risk exposure, autonomously selecting suppliers, conducting negotiations and tracking contract compliance. Its negotiation strategies continuously evolve based on environmental changes.
- Agentic route optimization: Agentic AI collects real-time data to find optimal routes, updating selections based on current conditions such as traffic, weather and fuel prices. By autonomously rerouting deliveries, it ensures timely arrivals and minimizes transportation costs.
Leading supply chains are differentiated by well-defined water stewardship strategies
As leading supply chain organizations harness the power of agentic AI and autonomous operations to optimize supply chain strategy, they are simultaneously recognizing the critical importance of resource stewardship, particularly water. As water emerges as a critical component of corporate and national security, many of the companies in this year’s Gartner Supply Chain Top 25 are differentiating themselves by developing well-defined water stewardship strategies and implementing water management, water conservation and water basin redevelopment initiatives.
According to CDP, 20% of companies report significant supply chain water risks. Water's strategic significance spans various industrial sectors, impacting value chains in agriculture, manufacturing and data centers due to its roles in crop raising, production and cooling. Despite its low-cost perception compared to energy and other materials, water is often undervalued, leading to overuse and adverse effects such as pollution and water table depletion. This undervaluation can obscure its true value, resulting in inefficient consumption and management practices.
Leading companies demonstrate their leadership by integrating water considerations into strategic decisions like site selection and supply chain design. By assessing water sources and discharges, aligning water management with growth plans and risk assessments and ensuring regulatory compliance, these companies enhance their water stewardship and bolster their supply chain's operational resilience.
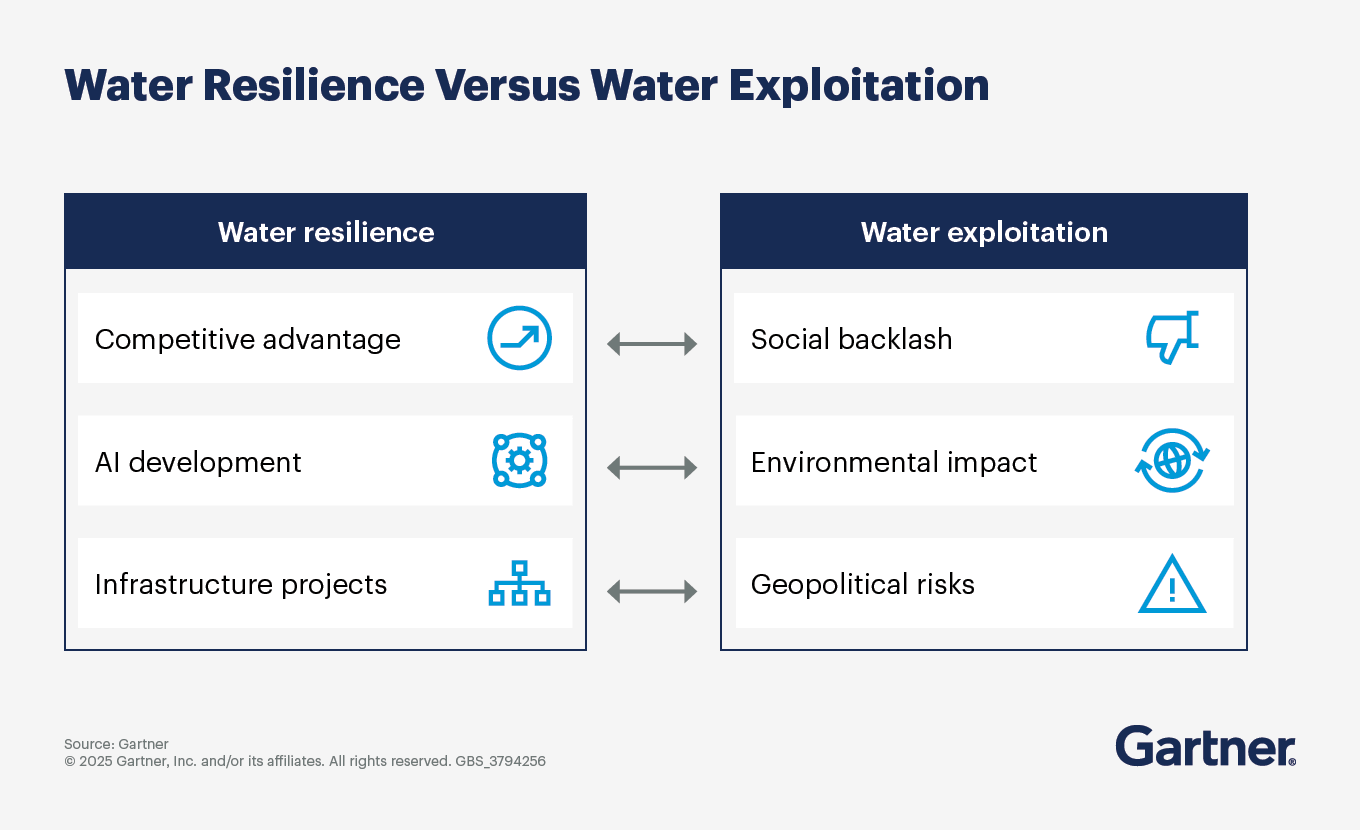
Strategic thinking guides operational investments, with companies embedding innovation into water strategies through technologies such as leak management, crop management, water loops, desalination and bio alternatives to water incineration. These initiatives indicate mature approaches to water resource management and future-focused strategies, incorporating scenario planning.
Establishing water stewardship strategies enhances scenario planning and risk assessment for water-dependent operations, fostering organizational resilience against supply chain disruption. Conducting climate change risk modeling to understand changing rainfall patterns is a crucial starting point for assessing water management strategies.
Embedding water management requirements across suppliers can enhance future resilience beyond direct operations. For instance, digital technology providers, heavily reliant on water availability, can be encouraged to adopt their own water management strategies, ensuring value chain resilience and efficient water use, leading to cost savings.
See more supply chain rankings by region and industry
Attend a Conference
Experience Supply Chain conferences
With exclusive insights from Gartner experts on the latest trends, sessions curated for your role and unmatched peer networking, Gartner conferences help you accelerate your priorities.
Gartner Supply Chain Symposium/Xpo™
Orlando, FL

Related resources: Gartner Supply Chain Top 25
The renowned ranking of the world’s superior supply chains is now in its 21st year.
FAQ on the Gartner Supply Chain Top 25
What is the Gartner Supply Chain Top 25?
The Gartner Supply Chain Top 25 is a renowned annual ranking of the world’s superior supply chains. Now in its 21st year, the Gartner Supply Chain Top 25 identifies, celebrates and profiles excellence in supply chain management. Supply chain teams use the Gartner Supply Chain Top 25 to benchmark performance, transform operations and lead in the future.
How are companies ranked in the Gartner Supply Chain Top 25?
A Top 25 supply chain ranking is based on an equal weighting of business metrics and community opinion.
Business metrics comprise financial and environmental, social and governance (ESG) metrics. Financial metrics are based on a combination of three-year weighted return on physical assets (ROPA), ROPA change and revenue growth, plus inventory turns across the year. ESG data is derived from trusted third-party sources in the areas of commitment, transparency and performance across each area of ESG.
Community opinion is based on the feedback of peer voters from the community and Gartner experts. Peer voters cast votes for their personal choice of the Top 25 supply chains. They base their decisions on perceived end-to-end supply chain maturity and leadership, specifically the supply chains that are run as strategic assets to deliver business and societal outcomes by partnering beyond their own organizations and that are thriving through uncertainty.
Learn more on gartner.com about the Gartner Supply Chain Top 25 methodology and how to participate in the community peer vote.
What benefits come from being in the supply chain rankings?
Ranking in the Gartner Supply Chain Top 25 is a point of pride and validation for the efforts of the supply chain team, as well as the company at large. The prestige that the Gartner Supply Chain Top 25 carries helps elevate the role of supply chain in the business and promote its innovation and leadership capability. A Top 25 supply chain ranking serves as a lever to attract, engage and retain critical supply chain talent, and may even be used as a performance management incentive.
How can my supply chain improve its chances of being ranked?
Consistent with the purposes of the Gartner Supply Chain Top 25 study, we believe that the sharing of best practices should be done through a transparent methodology that reflects a diversity of opinions. At a high level, the methodology combines financial performance and opinion data; the financials provide an objective basis on which to place community peer and Gartner analyst/expert votes. The methodology for the Gartner Supply Chain Top 25 is continuously evolving, growing in line with the supply chain profession.
The two parts of the research process in which supply chain companies can proactively participate are as follows:
Companies can submit a Supply Chain Research Information Packet (SCRIP). The SCRIP is completed online and allows companies to provide more specific insights into their supply chain strategies, organizational span and influence; key initiatives; and impacts supply chain has had on the success of the business.
Companies can also conduct a one-hour virtual company briefing. A virtual company briefing serves as an opportunity for an interactive session with the Gartner analysts/experts who are voting to discuss their supply chain initiatives in more detail.
The criteria for 2025 (revenue threshold, financial data, industry, community sentiment and awareness and ESG threshold) remain unchanged from last year. Nor are we making any substantive changes to the methodology, as we wish to give companies the opportunity to compare their year-over-year composite scores and demonstrate progress from a stable base. The only change we will be making for 2025 is to replace the Bloomberg Gender Equality Index, which accounted for one of the points available for ESG Social Performance. In its place, we will be adopting a broader social dimension derived from the S&P ESG Social Score.
Drive stronger performance on your mission-critical priorities.