Enhance HR tech efficiency and innovation in human resources.
- Gartner client? Log in for personalized search results.
HR Technology: Best Practices & Its Role in HR Management
Turn HR technology into your competitive edge
Only 35% of HR leaders are confident their approach to technology is helping them achieve business objectives.
Download this guide to learn how CHROs are rethinking HR technology strategy to advance transformation goals.
Understand why typical approaches to HR technology don’t deliver.
Learn the three actions you can take to maximize technology’s value.
See how HR leaders of real-world brands apply these actions to drive better results.
See Gartner research in action at our HR conferences and events.
Use HR technology to solve what’s holding your business back
CHROs: A robust HR technology strategy is imperative to drive organizational growth, attract and retain top talent, and secure your competitive advantage.
Empower Your Organization
Adopt AI for HR
Map Your HR Tech Strategy
Demystify Tech Vendors
HR tech drives business value by enhancing employee journeys and efficiencies
Today’s businesses expect HR to create new value that goes beyond traditional HR processes and expectations. To create more business value from digital HR, CHROs need to maximize three business value levers: employee experience (EX), productivity and well-being.
Understanding how HR technology is changing the workplace is critical, as it impacts the day-to-day work of each employee and has enormous potential to improve work outcomes.
To drive greater business value from your HR technology, use the following three-step approach.
Step 1. Define employee work journeys
Most employees have similar HR journeys — such as recruitment, onboarding, assessment and pay cycles — but have very different day-to-day work processes and technologies. The experience employees have in their individual work journey will dramatically impact the three business value levers.
For a better understanding of the day-to-day and where challenges exist, engage employees through focus groups, individual interviews, workshops, and HR data and work systems.
Step 2. Collaborate across functions
Once you’ve identified work journey challenges for employees, work with organizational partners to mitigate those challenges. Employees with a positive EX are 54% more likely to stay at the organization and almost 55% more likely to be high performers. But HR can influence only certain parts of the employee experience.
To get each function aligned on challenges and solutions, create cross-functional fusion teams that connect leaders with team members from HR.
Step 3. Choose digital technologies that enable solutions
HR technology solutions for work journey challenges span both HR and non-HR technologies. For example, internal talent marketplaces match talent to opportunities like gigs, project roles, job shadowing, etc.
Focusing on a specific challenge within the business (for example, manufacturing needs new skills), work with other teams and technologies to find opportunities for skills mentoring, part-time work and internal mobility. Then HR can use internal talent placement technologies to match people to those open opportunities and create new business value.
Adapt to tech changes with AI to enhance HR efficiency and employee experience
Every HR organization faces multiple priorities: Addressing the changing landscape of technology, people and work, responding to demands for greater talent and skills, and delivering a human-centric EX. Although the magnitude of change can put a strain on most HR technology portfolios, it has also spawned a range of solutions that highlight the benefits of HR technology.
The emergence of AI in HR — with its many use cases and impacts — creates the need to assess which technologies are most relevant to your desired HR and organizational outcomes.
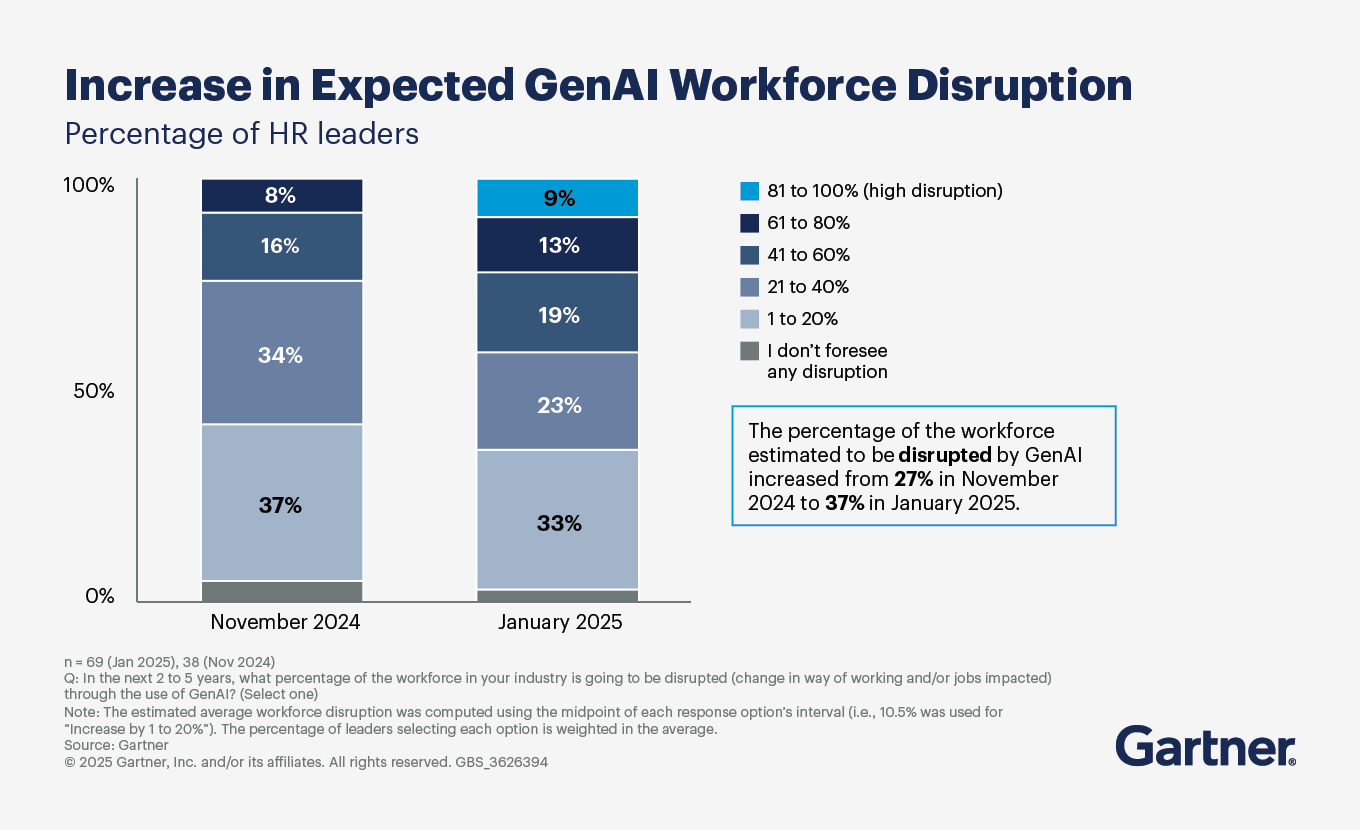
The hype around GenAI has peaked, and so has HR leaders’ interest in this technology. Sixty-two percent of HR leaders were in the latter stages of the GenAI implementation funnel in January 2025. In the HR domain, primary goals for GenAI are to improve efficiency (77%), improve the employee experience (52%) and enhance decision making (43%).
As you explore AI-driven HR technology platforms for your organization, consider these four key recommendations:
Experiment incrementally with GenAI. Work with key business stakeholders to evaluate the technology’s benefits, impact and maturity for each HR use case, rather than pursuing rapid, large-scale GenAI adoption throughout the function.
Collaborate with legal and compliance partners, as well as vendors, to identify potential risks and biases for each GenAI use case. Some solutions, such as GenAI in talent profiles, may require time to mature in this rapidly evolving technology space.
Establish responsible use of GenAI in HR by implementing policies, procedures and other governance mechanisms that address regulatory and legal requirements, in addition to ethical considerations, now and as they continually emerge.
Select initial use cases by prioritizing low-risk, more mature capabilities. Choose vendors with detailed roadmaps, comprehensive guidelines and open disclosure of vulnerabilities, possible harms and misuse scenarios.
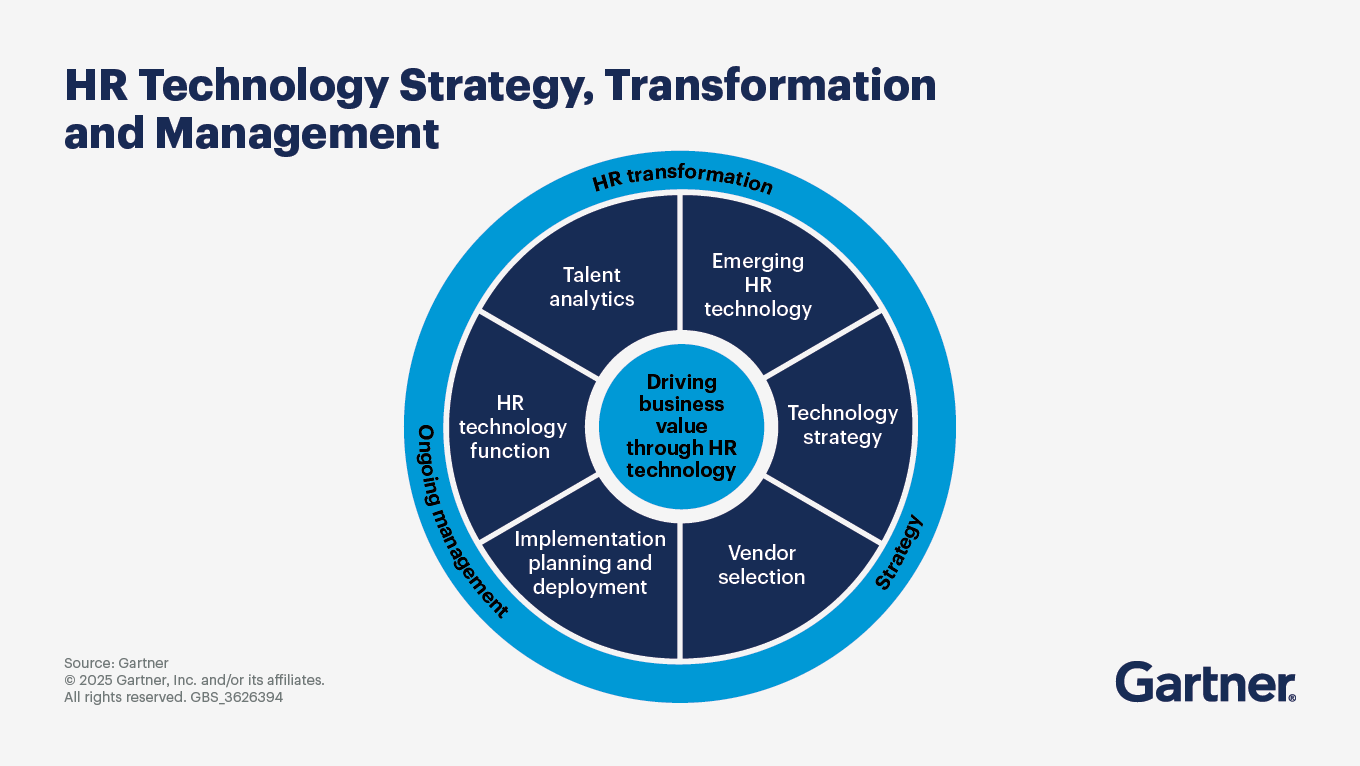
Create a vision, analyze options and chart your path for HR tech success
Without a robust, updated HR technology strategy and roadmap, aligning HR technology investments with business needs can be challenging.
Take a structured approach by working with HR technology leaders to engage stakeholders, prioritize outcomes, analyze technology options and create an effective roadmap. The following three-step framework will help with creating a strategic roadmap that incorporates best practices for leveraging HR technology.
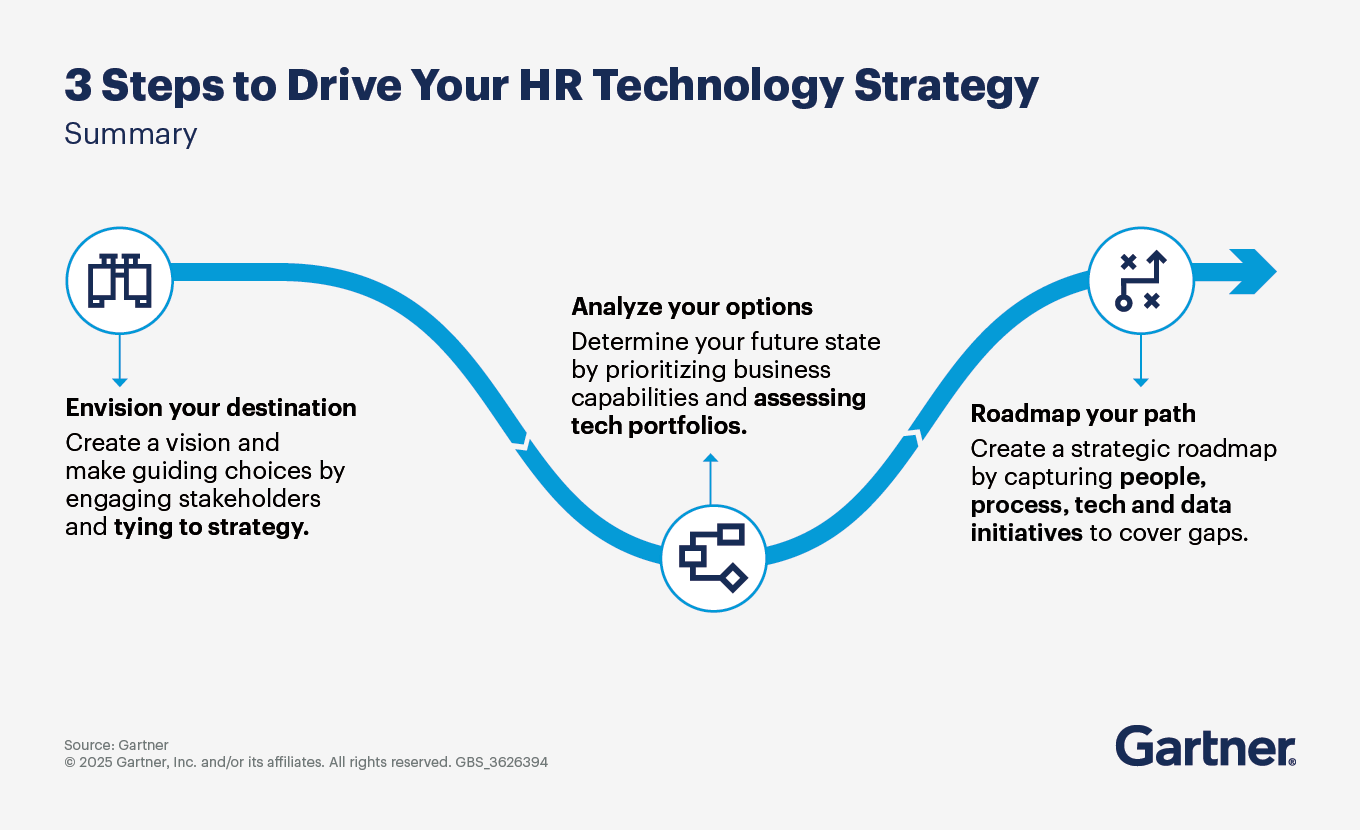
Step 1: Envision your destination
Create a vision and make guiding choices by engaging stakeholders and prioritizing outcomes, ensuring a strategic HR technology implementation. First, tie broader business outcomes to broader HR outcomes and then to specific HR technology outcomes.
For example, if your CEO’s goal is revenue and profit growth, this leads to an HR goal of talent attraction, development and retention. HR technology would need to support these goals by providing enhanced candidate and employee experiences. Prioritizing HR technology outcomes is a necessary prerequisite to evaluating technology options.
For an overall strategy, identify an HR technology vision that is either process-led (making sure that process excellence is being met) or experience-led (making sure that users find it very simple to accomplish any and all HR-related tasks), likely with a cross-process user view.
Then consider what “guiding choices” matter most to your organization. For example: Would you value stability over innovation? Are you prioritizing end-user experience or process enablement?
Step 2: Analyze your options
Determine your optimal future state by prioritizing business capabilities and assessing technology portfolios.
Pair your HR vision with your execution profile:
Portfolio-based: Tech decisions are oriented to looking for the best solution for the capability, avoiding overreliance on a single provider.
Suite-centric: HR technology investment decisions are put through a “why not the suite” or “suite-first” lens.
Your vision and execution will determine your cohort, each with its own attributes:
Centralized cohorts (process-led, suite-centric) offer streamlined but limited tech enablement and simple but limited employee experience.
Consolidated cohorts (experience-led, suite-centric) offer more complex technology due to extensions and limited access to innovation.
Augmented cohorts (process-led, portfolio-based) offer deep but siloed tech enablement and disjointed employee experience.
Optimized cohorts (experience-led, portfolio-based) offer deep and orchestrated tech enablement and a journey-like employee experience.
Step 3: Map your path
Create an HR technology roadmap to the future state by capturing critical people, process, technology and data initiatives to cover gaps.
Identify your current cohort, where you’d like to be in three years and what people, processes and technology you need to make the journey.
Take the high-priority HR business capabilities and determine what gaps you want to address to arrive at your target future state. Specifically map out which gaps will be addressed over the next three years.
For example, you might identify a lack of IT skills (people gap) or ineffective policies (process gap). Evaluate all the possible technology solution markets that could fill those gaps, as well as the timing of the initiative (strategy, technology and business readiness, implementation, etc.).
Navigate the complexities of HR technology and vendor selection
Selecting, implementing and managing HR technology is both complex and time-consuming. Overcome competing internal priorities, avoid some of the challenges faced in adopting HR technology, and make more confident decisions by working with HR technology leaders to demystify the complex vendor landscape.
As you work with your team to understand the tech landscape and choose tech vendors, consider incorporating the following best practices:
Be sure the evaluation team includes a mix of functional, technical and line-of-business (LOB) staff, as well as “typical” employees and managers. This resource mix is especially critical to properly assess how emerging HR technology solutions, such as applied AI, HR virtual assistants and hyperautomation, might affect solution user experience (UX) and overall EX.
- Confirm your understanding of desired outcomes by using critical use cases and business capabilities modeling to drive detailed requirements for RFI/RFP and vendor demonstration scripts.
Direct the vendor demos and include time for test-driving by primary end users. Schedule follow-up sessions (technical, implementation and support) with vendors to cover any topics not completely addressed during the primary demos.
Review and scrutinize to what degree the solution’s customer community has influenced product direction and affected the vendor’s subsequent delivery of product enhancements.
Attend a Conference
Join Gartner experts and your peers to accelerate growth
Gather alongside your peers in Orlando to gain insights on emerging trends, receive one-on-one guidance from a Gartner expert and create a strategy to tackle your priorities head-on.
Gartner HR Symposium/Xpo™
Orlando, FL

HR Technology FAQs
What is HR technology?
HR technology encompasses software and tools that automate and streamline human resources tasks. It includes systems for recruiting, onboarding, payroll, performance management and employee engagement. By leveraging HR technology, organizations can enhance efficiency, improve data accuracy and provide better employee experiences. This technology empowers HR professionals to focus on strategic initiatives rather than administrative tasks.
What are the key HR technology trends for 2025?
Key HR technology trends for 2025 include AI-driven recruitment, personalized employee experiences, and advanced analytics for decision making. Companies will adopt remote work solutions, integrate wellness programs and utilize blockchain for secure data management. Automation will streamline HR processes, while mobile-friendly platforms will enhance accessibility. These trends aim to boost efficiency, engagement and data security in HR operations.
How does technology enable data-driven HR decisions?
As enterprise organizations advance their HR technology strategies, HR technology leaders are increasing their spend on reporting and analytics platforms to connect HR system capabilities with key business and talent outcomes.
Talent analytics is one example. HR can use tech-enabled talent analytics to inform leader decisions and enhance talent outcomes. And talent management leaders use predictive analytics to provide insights on attrition, burnout, employee sentiment and other metrics.
What role does AI play in HR practices?
AI in HR technology has a multitude of use cases. Some of these include the following:
Talent acquisition. AI-powered candidate assessments can infer a candidate’s cognitive traits, behaviors, emotions or personality. AI also aids in sourcing and ranking candidates and job fit scoring.
Voice of the employee. Natural language processing techniques are used to identify employee-experience-focused themes and sentiment.
Learning. AI-powered HR software can deliver personalized learning recommendations based on learner behavior.
How does HR technology enhance the hiring process?
HR historically relied on an applicant tracking system to meet the core tracking, posting and automation requirements of the hiring process. As the talent acquisition function of many organizations has expanded to compete for talent, HR technologies now cover a broader set of activities, such as recruitment marketing, candidate relationship management, onboarding and even internal talent marketplaces.
Because of pressing hiring needs for most organizations, using HR technology for passive-candidate sourcing, AI-enabled candidate skills matching, interview-related automation and improving the overall candidate experience has the highest potential for enhancing the hiring process.
Drive stronger performance on your mission-critical priorities.